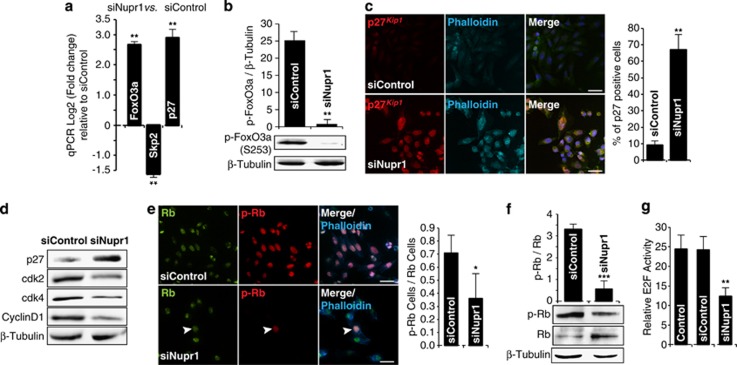
Figure 3.
Nupr1 depletion triggers the FoxO3a-Skp2-p27Kip1 pathway. (a) By RT-qPCR, increase of FoxO3a, which negatively regulates Skp2, decrease of Skp2, which degrades p27Kip1, and consequently increases of p27Kip1 transcript is observed in Nupr1-depleted cells. (b) Phosphorylated FoxO3a, by western blot, in siNupr1 or siControl MiaPaCa2-treated cells. (c) Positive nuclear immunofluorescence of p27Kip1 is observed in siNupr1-treated cells. No signal is observed in cells upon siControl treatment. (d) Western blot shows the increase of p27Kip1 protein and decrease of Cdk2, Cdk4 and cyclin D1 in cells depleted of Nupr1. (e) Immunofluorescence of Rb (green) and phospho-Rb (Red) proteins in MiaPaCa2 cells. In siControl-treated cells, all cells present the phosphorylated form of Rb. On the contrary, only one cell (arrowhead) is positive for phospho-Rb in Nupr1-depleted cells. (f) Western blot showing the increase of the active hypophosphorylated form of Rb in MiaPaCa2 cells. (g) Reporter gene assay for E2F transcription factors. Significant decreased activity is observed when cells are silenced for Nupr1. Error bars±S.D.; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. Scale bar, 10 μm