Figure 2.
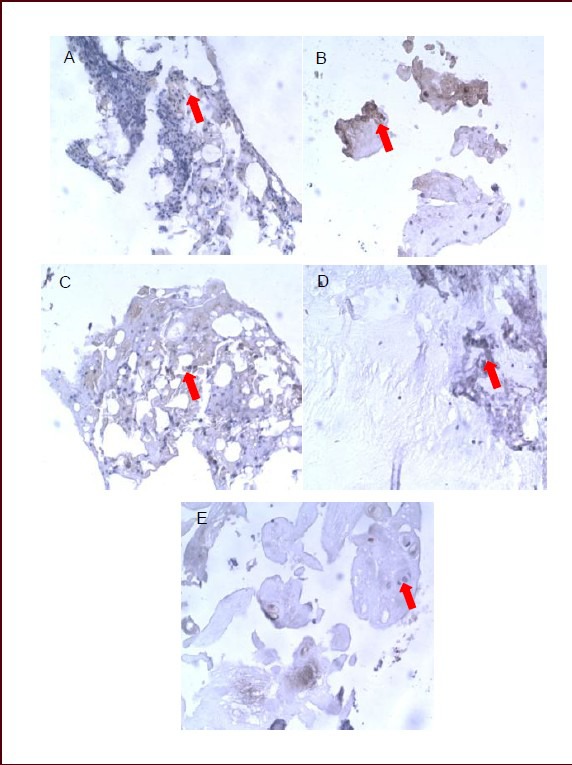
Effects of sciatic nerve defect on calcitonin gene-related peptide expression in L5 dorsal root ganglia of rats (immunohistochemical staining, streptavidin-biotin complex, × 400).
Light microscopy showed that calcitonin gene-related peptide-positive products (arrows) stained dark yellow or brown, mainly distributing in fibrous tissue.
(A) Calcitonin gene-related peptide-positive products were dense and darkly stained in the dorsal root ganglion of normal rats at 7 days.
No significant difference was found in staining or distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide-positive products between 14 (B) and 7 days (A) in the dorsal root ganglion of normal rats.
(C) Calcitonin gene-related peptide-positive products stained darker and significantly increased in rats with sciatic nerve injury than in normal rats at 7 days.
Expression of calcitonin gene-related peptide was reduced and the staining became lighter in rats with sciatic nerve injury at 14 days (D) compared with 7 days (C), but remained higher than in normal rats.
(E) Expression of calcitonin gene-related peptide in rats with sciatic nerve injury was similar to that in normal rats at 28 days.
