Figure 5.
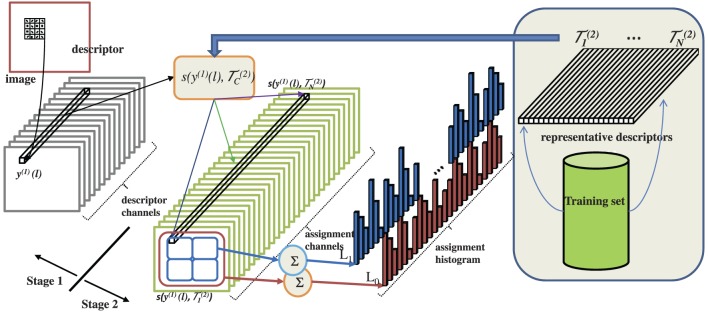
Canonical architecture implemented by various popular object recognition methods. Images are represented by sets of descriptors. A set of representative descriptors {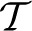 (2)c} is learned from an image training set. The descriptors y(1)(l) extracted from the image to classify are then encoded, with respect to this set of representatives. The encoding consists of assigning each descriptor to a subset of the representatives, using a similarity function s(y(1)(l),
(2)c} is learned from an image training set. The descriptors y(1)(l) extracted from the image to classify are then encoded, with respect to this set of representatives. The encoding consists of assigning each descriptor to a subset of the representatives, using a similarity function s(y(1)(l), 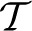 (2)c). This could be a probabilistic function, e.g., probability under a Gaussian mixture model, or a sparse encoding. The assignments are finally pooled spatially to produce assignment histograms, which are fed to a classifier, e.g., a support vector machine.
(2)c). This could be a probabilistic function, e.g., probability under a Gaussian mixture model, or a sparse encoding. The assignments are finally pooled spatially to produce assignment histograms, which are fed to a classifier, e.g., a support vector machine.
