Figure 6.
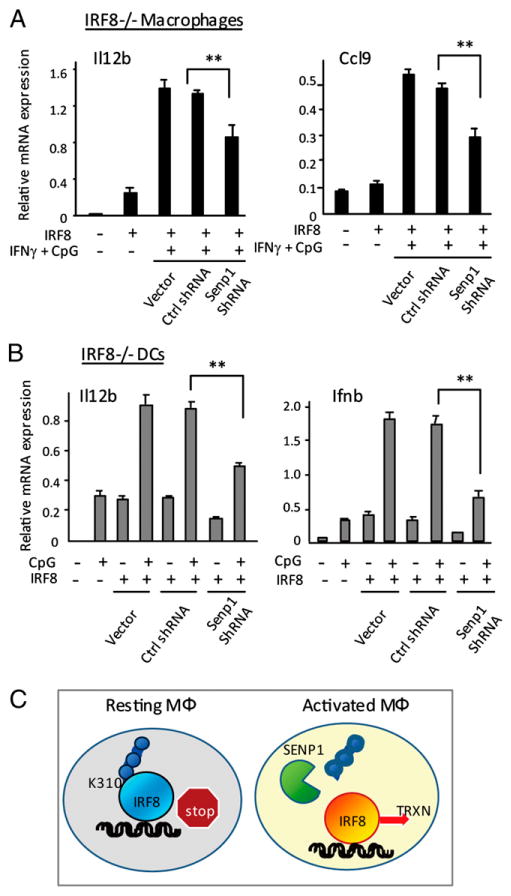
SENP1 knockdown inhibits IRF8 transactivation. (A) CL2 cells were transduced with pMSCV vector for wt IRF8, along with empty vector, control shRNA, or Senp1 shRNA pSuper vector, and cultured for 5 d, followed by stimulation with IFN-γ/CpG. Expression of indicated genes was measured by qRT-PCR, as above. (B) IRF8−/− BM DCs (106 cells) were transduced with viral vectors, as above, and stimulated with CpG for 4 h. The values represent the average of three determinations ± SD. Statistical significance was tested by Student t test; **p < 0.005. (C) SUMO conjugation-deconjugation switches IRF8 function: a model. SUMO-conjugated IRF8 present in resting macrophages acts as a repressor. Activation of macrophages with IFN-γ or IFN-γ/TLR stimulates SENP1 expression. SENP1 then removes SUMO from IRF8, converting it to a transcriptional activator. This SUMO switch is critical for the induction of IRF8-regulated genes.
