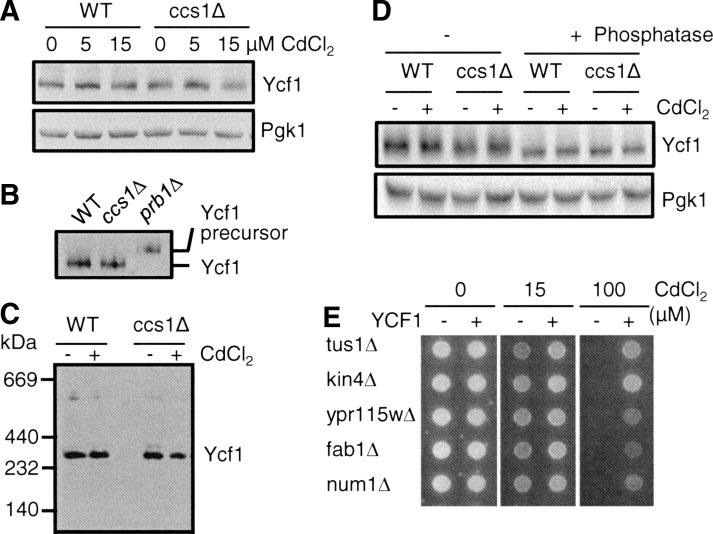
FIG. 6.
Effects of CCS1 deletion and cadmium co-culture on post-translational events of Ycf1p. (A) WT and ccs1Δ cells expressing C-terminal HA-epitope-tagged functional Ycf1p were co-cultured with the indicated concentration of CdCl2 for 9 h. Total cell lysates prepared by vortexing the cells with glass beads were solubilized with 1% Triton X-100 and subjected to SDS-PAGE, and Ycf1p was detected by western blotting using anti-HA antibodies. To determine equal loading, each blot was also probed for 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (Pgk1p). (B) N-terminal proteolytic processing of Ycf1p. C-terminal HA-epitope-tagged functional Ycf1p was expressed in wild-type control (WT), ccs1Δ, and prb1Δ cells. Lysates extracted from the mid-log phase cells that were cultured in SC selection media were subjected to western blotting using anti-HA antibodies. (C) Ycf1p is detected as predicted homo-dimers. WT and ccs1Δ cells expressing HA epitope-tagged Ycf1p were co-cultured with CdCl2 (15 μM, 9 h). Ycf1-enriched fractions obtained by sucrose density gradient centrifugation of cell lysates were subjected to blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by western blotting using anti-HA antibodies. (D) Phosphorylation-dependent migration change of Ycf1p on SDS-polyacrylamide gel. WT and ccs1Δ cells expressing HA-epitope-tagged Ycf1p were cultured with or without CdCl2 (15 μM, 9 h) in the media. Cell lysates with or without phosphatase treatment were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Ycf1p was detected by western blotting using anti-HA antibodies. Dephosphorylated Ycf1p migrates fast. (E) YCF1-dependent cadmium resistance in the strains deleted for indicated genes encoding proteins that physically interact with Ycf1p. The strains expressing an empty vector or YCF1 expression construct were spotted on SC selection media that was supplemented with CdCl2. Cell growth was photographed after 2 days. Experiments were conducted at least twice with two different clones, and a representative figure is shown.