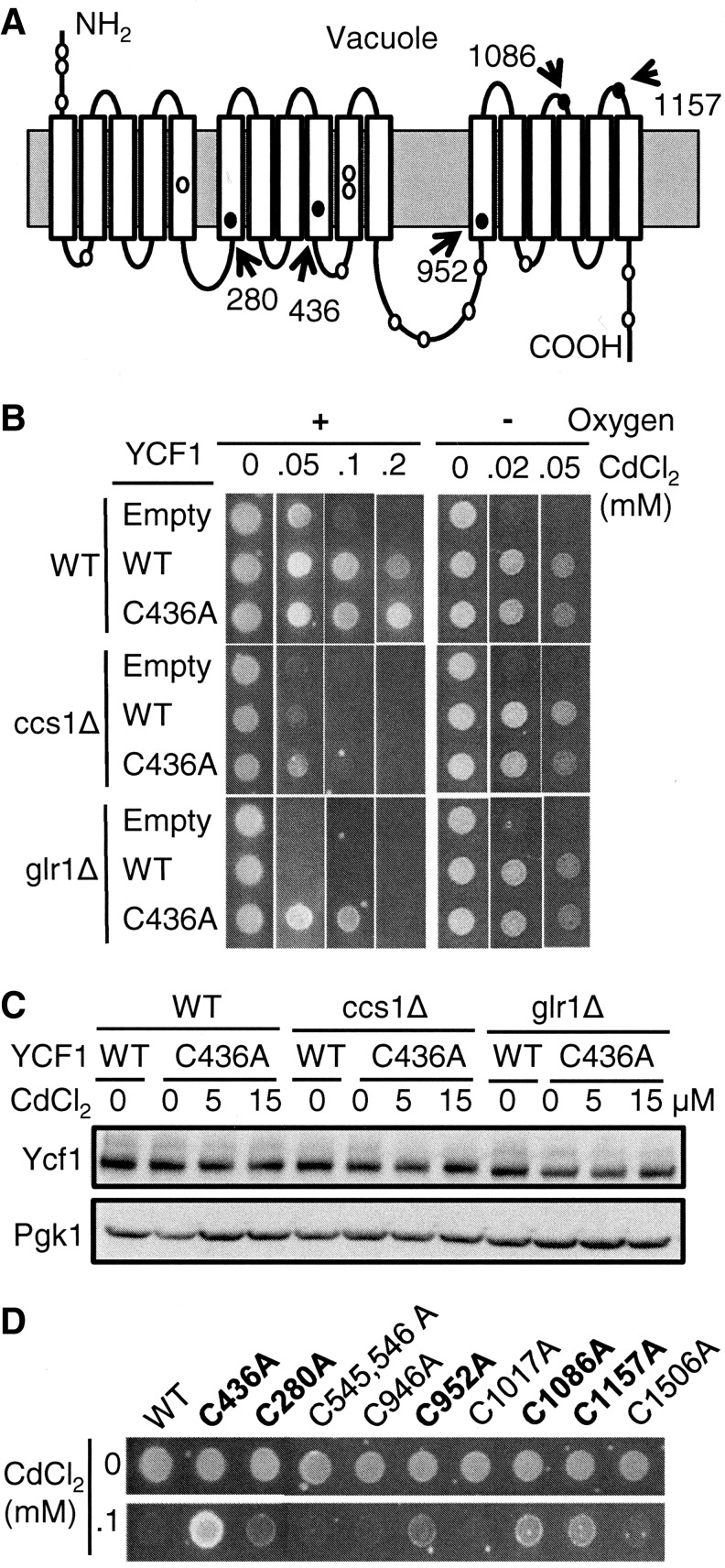
FIG. 7.
Cysteine residues in Ycf1p affect its activities in antioxidant and oxygen-dependent manners. (A) Schematic depiction of the structural features of Ycf1p and location of the 20 Cys residues. Ycf1p contains 17 predicted transmembrane helices (white boxes). Cysteine residues are labeled as circles, and five of them that affect Ycf1p function in ccs1Δ or glr1Δ cells are filled with black. (B) YCF1(C436A) confers cadmium resistance when expressed in ccs1Δ and glr1Δ cells. WT control, ccs1Δ, or glr1Δ cells expressing an empty vector or YCF1(C436A) were cultured to the mid-log phase. Cells (∼5 μl of OD600=0.5) were spotted on SC selection media that was supplemented with indicated CdCl2 concentrations. Plates were cultured aerobically and anaerobically for 2 and 4 days, respectively, before photography. (C) Expression of Ycf1p determined by western blotting. WT, ccs1Δ, and glr1Δ cells expressing empty vector, YCF1, or YCF1(C436A) were co-cultured with CdCl2 (15 μM, 9 h). Cell lysates were prepared by vortexing cells with glass beads in the buffer containing 1% triton X-100. Samples were subjected to western blotting using anti-HA antibodies. To determine equal loading, each blot was probed for 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (Pgk1p). (D) Expression constructs of YCF1 possessing Ala substitution of indicated Cys residues were transformed into glr1Δ cells. Cell growth on cadmium-containing media was photographed in 2 days. YCF1 alleles that confer a better cadmium resistance relative to control YCF1 are highlighted in bold.