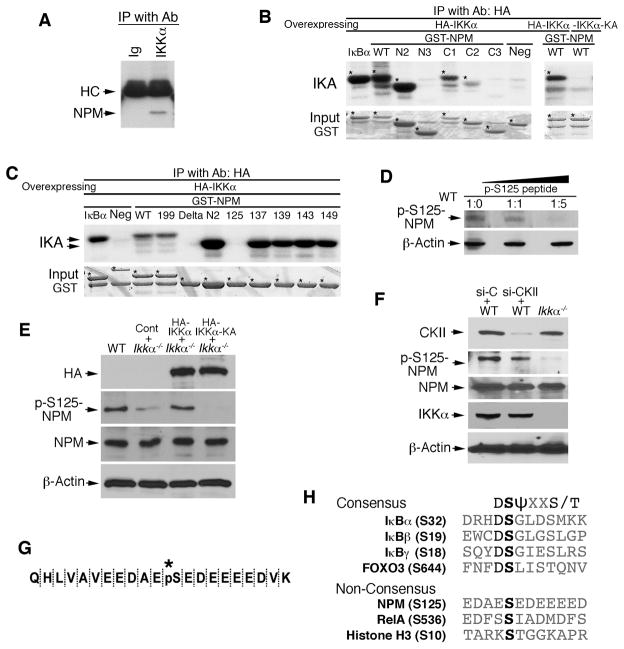
Figure 1. NPM Interacts with IKKα and Phosphorylates S125 of NPM.
(A) Interaction of IKKα and NPM in primary cultured keratinocytes detected by immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-IKKα antibody (Ab) and western blot with anti-NPM antibody. Immunoglobulin (Ig), control for IP; HC, antibody heavy chain.
(B–C) Phosphorylation of NPM by IKKα was analyzed with an immunocomplex kinase assay (IKA). HA-IKKα was precipitated with anti-HA antibody using lysates of HEK293 cells overexpressing HA-IKKα or HA-IKKα-KA. GST-NPM proteins were used as kinase substrates. Five phosphorylation sites within aa 119–195 of NPM were examined using IKA. GST IκBα, positive control for IKK; Neg, GST-14-3-3σ protein as a kinase-negative control; *, bands indicating labeled proteins.
(D) The specificity of p-S125-NPM from WT MEF lysates was analyzed by western blot with anti-p-S125-NPM antibody that was incubated with a specific p-S125-NPM peptide for 2 hr at room temperature. β-Actin, protein-loading control. Ratio, antibody:peptide.
(E) Western blot shows HA-IKKα (HA), p-S125-NPM and NPM levels in WT and Ikkα−/− MEFs transfected with HA-IKKα, HA-IKKα-KA, or control vector (Cont).
(F) Western blot shows CKII, p-S125NPM, NPM, and IKKα levels in Ikkα−/− and WT MEFs treated with control siRNA (si-C) or CKII siRNA (si-CKII).
(G) Phosphorylated S125-NPM sequence (*, pS) was analyzed using trypsin digestion and mass spectrometry.
(H) The consensus sequences containing serine sites that can be phosphorylated by IKKα and IKKβ. S, serine; D, aspartic acid; T, threonine; ψ, hydrophobic amino acid; X, any amino acid. See also Figure S1.