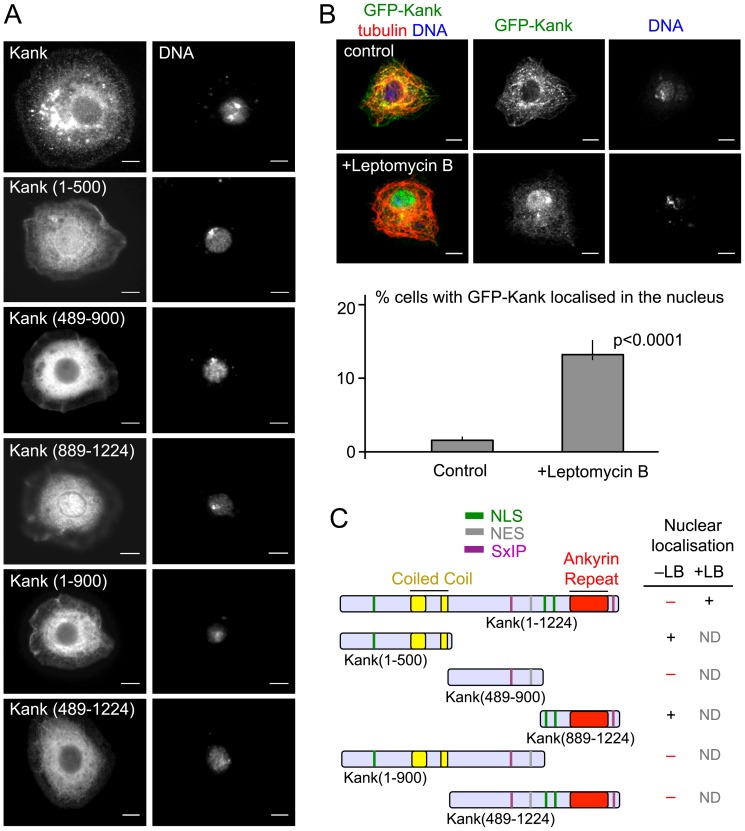
Figure 3. Kank can localise transiently to the nucleus of S2 cells.
(A) Kank(1–500) and Kank(889–1224) exhibit nuclear localisation, while truncations of Kank which contain the middle region do not. S2 cells were transfected with GFP-fused Kank truncations. Cells were then co-stained for GFP, α-tubulin and DNA. (B) Kank shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in some cells. S2 cells transfected with GFP-Kank were incubated with media containing leptomycin B for 3–3.5 hours, to inhibit nuclear export. Control cells were incubated with media containing methanol, the solvent for leptomycin B. Nuclear localisation was observed more frequently in leptomycin B treated cells than control cells. Significance was determined by Fishers exact chi squared test. Error bars show the 95% confidence interval. (C) A summary of Kank truncations and their nuclear localisation. + and – indicate the presence and absence of the nulcear localisation with (+LB) or without (–LB) Leptomycin B. ND (Not done). Scale bars = 5 µm.