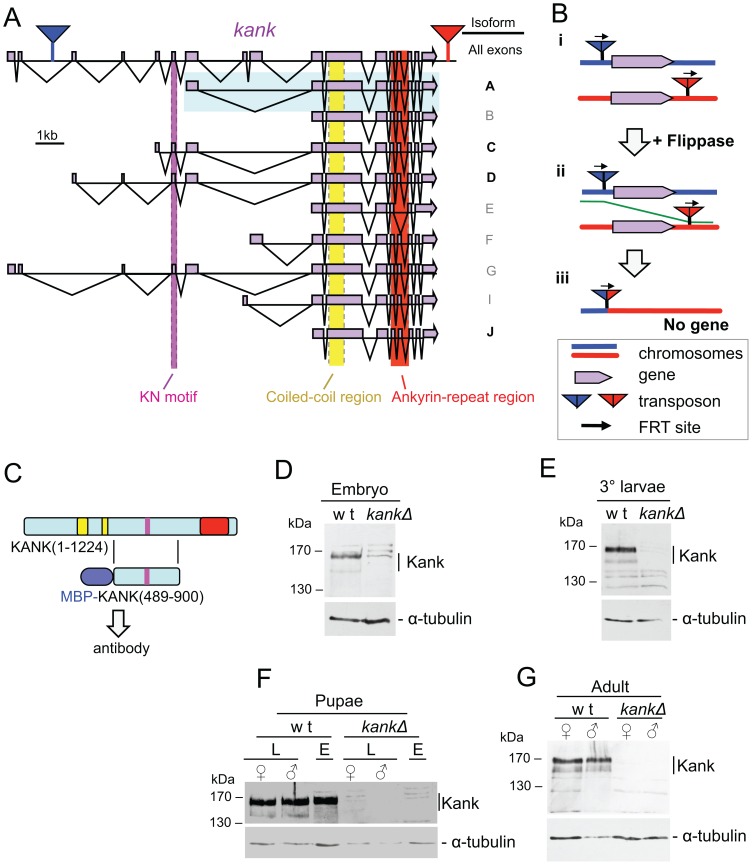
Figure 4. Kank is expressed throughout development but is dispensable for viability and fertility.
(A) kank (CG10249) is a ∼27 kb gene found at 51D2 on chromosome arm 2R. Putative isoforms are shown. Those in black are likely to be expressed while those in grey are less likely to be expressed based on ModEncode data. The cDNA clone GH03482 that we used in our analysis represents isoform A of kank (highlighted in blue). This isoform lacks the KN motif found in other Kank proteins (shown in purple). (B) Kank was deleted using transposons containing FRT sites. Firstly, the appropriate two transposons flanking the Kank coding sequence were introduced in trans positions on homologous chromosomes (i). A flippase was induced to promote recombination between the FRT sites (ii) and generated a deletion of the intervening sequence (iii) (C) The fragment of Kank(489–900) used for generating an antibody against the Kank protein. (D–G) The Kank antibody detected the endogenous protein in all lifecycle stages examined by immunoblotting in wild type but not in Kank deletion mutants. Kank was detected in embryos 21–24 hrs after egg laying (D), in 3rd instar larvae (E), in male and female late pupae [ = L] and early pupae of undetermined gender [ = E] (F), and in both male and female adult flies (G).