Figure 8.
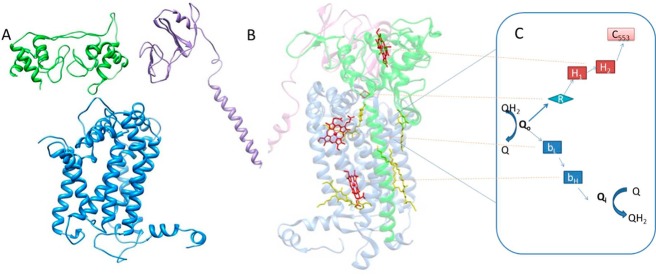
(A and B) Assumed dimer of the H. modesticaldum cytochrome bc complex: blue for the cytochrome b subunit, purple for the Fe–S subunit, and green for the cytochrome f subunit. (A) Imagined left half of dimer shown as homology-modeled subunits of the H. modesticaldum cytochrome bc complex. (B) Right side of the dimer shown as the determined crystal structure of the cytochrome bc1 complex from Rhodobacter sphaeroides used as the template for Figure 8A. Heme cofactors are colored red. (C) Proposed H. modesticaldum cytochrome bc complex bifurcated electron-transfer steps and mechanism: Q for quinones, Qo for the quinone oxidation site, Qi for the quinone reduction site, R for Rieske Fe–S, bL,H for b-type hemes, H1,2 for DHCC c-type hemes, and c553 for electron acceptor soluble cytochrome c553.
