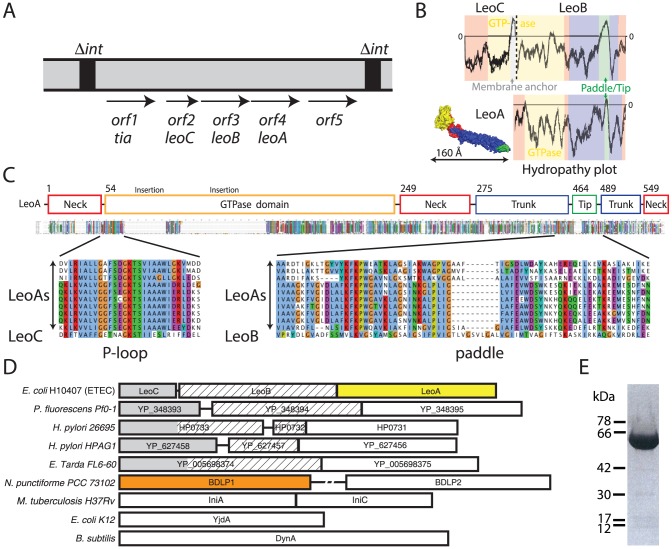
Figure 1. LeoA is part of a conserved putative operon.
A: overview of the tia locus in E. coli ETEC H10407; modified from [13]. An annotated version of the locus with probable promoter and RBS sites is shown in Figure S1 in File S1. B: Surface plot of the LeoA monomer coloured by domains: yellow, GTPase domain; red, neck domain; blue, trunk domain; green, putative paddle region. Similarly coloured hydropathy plots (TMpred) provide transmembrane prediction for LeoA and LeoB, respectively. C: Orf2 and orf3 of the tia locus align well against orf4, which encodes LeoA and the alignment spans the entire length of LeoA. It seems that LeoA is encoded in tandem with another in sequence related orf that is split into two chains. Orf2 and orf3 have been renamed here leoC and leoB, respectively. Sequences aligned: LeoA (E. coli ETEC H10407), WP_011717023.1 (Shewanella sp. ANA-3), WP_007214706.1 (Bacteroides cellulosilyticus), WP_001006159.1 (Helicobacter pylori), WP_001006151.1 (Helicobacter pylori), WP_014535968.1 (Helicobacter pylori), WP_000787447.1 (Helicobacter pylori), WP_001006093.1 (Helicobacter pylori), WP_000787451.1 (Helicobacter pylori), WP_005966123.1 (Fusobacterium periodonticum). D: Tandem genes for bacterial DLPs are common. Previously reported were IniA and IniC, and DynA, which is a fusion of two DLP genes [37]. Nostoc BDLP1 occurs in tandem with BDLP2 [6]. YjdA does not seem to follow this pattern. LeoABC shows splitting of the first gene into two as shown in Figure 1B and C. Dimensions are approximate. A large non-coding region (525 bp) between BDLP1 and BDLP2 is indicated. E: Purified His6-tagged LeoA protein, over-expressed in E. coli and purified by metal affinity and size exclusion chromatography.