Figure 1.
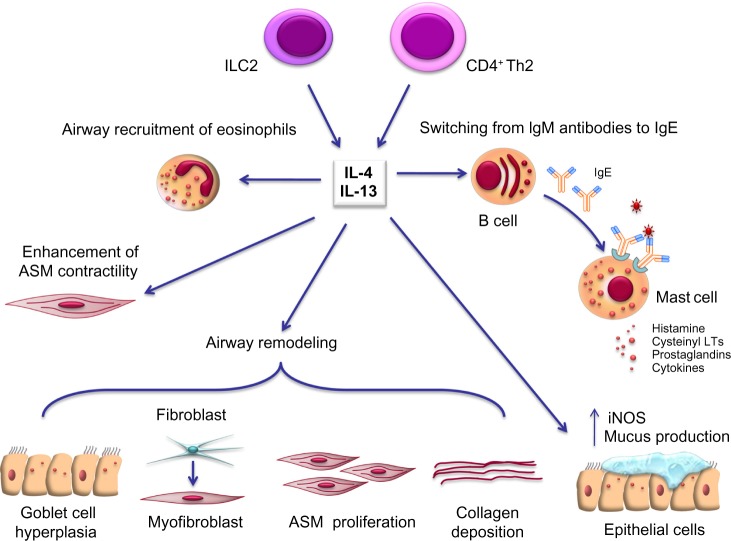
Pleiotropic effects of IL-4 and IL-13 in asthma pathobiology. See text for details.
Note: Mainly produced by CD4+ Th2 cells and type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), IL-4, and IL-13 act on several cellular targets within the airways of asthmatic subjects. In particular, these two cytokines induce B lymphocytes to synthesize large amounts of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies, and also promote the recruitment of eosinophils. Moreover, IL-13 elicits airway epithelial cell expression of iNOS, mucus production and goblet cell hyperplasia, stimulates ASM contraction and proliferation, and also enhances extracellular deposition of collagen and fibroblast to myofibroblast phenotypic transition. All these effects of IL-4 and IL-13 significantly contribute to airway inflammation and remodelling in asthma.
Abbreviations: ASM, airway smooth muscle; IL, interleukin; LTs, leukotrienes; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase.