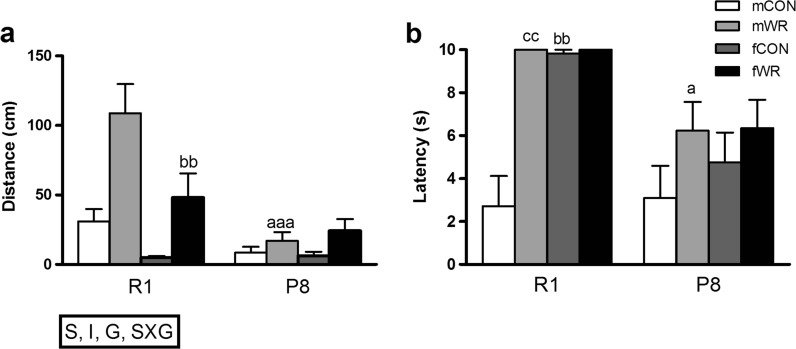
Fig. 4.
Evaluation of the sensorimotor status of R1 and P8 mice. a Overall, R1 mice showed better performance than P8 mice on the balance test (S: strain effect, p < .001; mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of the distance travelled on the flat and circular rod), WR mice travelling further distances in the rods (I: intervention effect, p < .001), male mice showing better balance than female mice (G: gender effect, p < .05), this effect being greater in R1 male mice (SXG: strain × gender interaction, p < 0.01). aaa p < .001 versus the corresponding R1 group (same gender and type of intervention); bb p < .01 versus the corresponding male group (same strain and type of intervention). b WR intervention improved muscular strength in R1 and P8 mice (mean ± SEM of the latency scored in the hanging test); a p < 0.05 versus the corresponding R1 group (same gender and type of intervention), bb p < .01 versus the corresponding male group (same strain and type of intervention), cc p < 0.01 versus the corresponding CON group (same strain and gender)