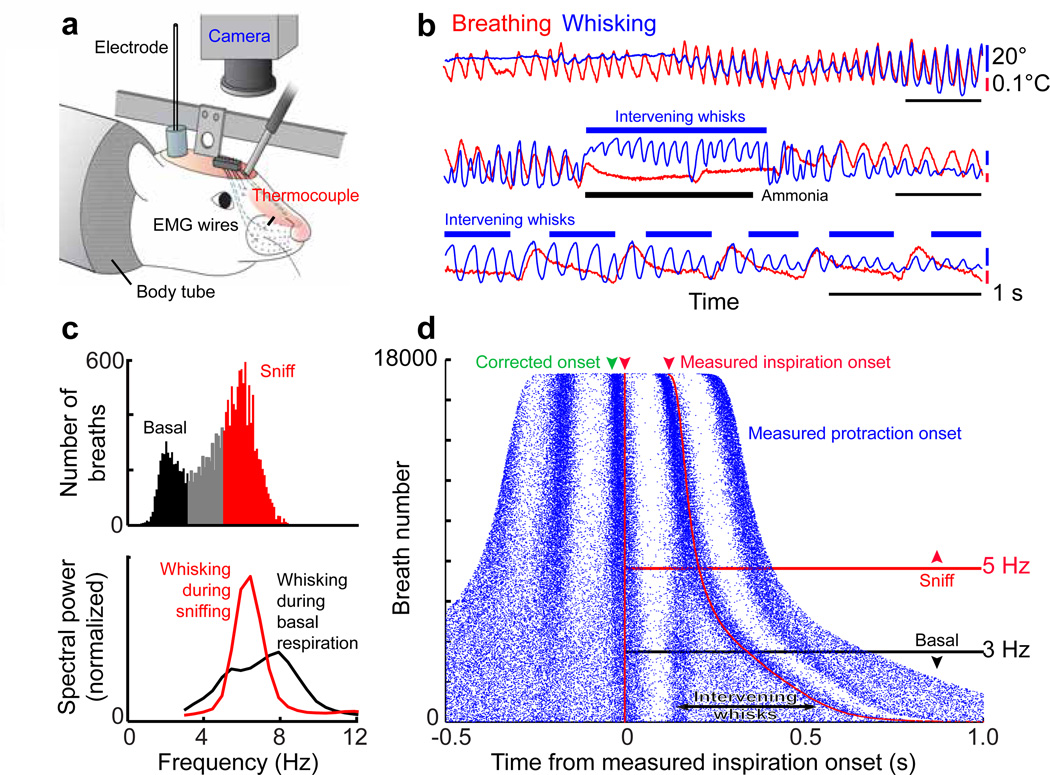
Figure 1. Coordination of whisking and breathing.
(a) Procedures to measure whisking, breathing, and associated electrophysiology in headrestrained rats.
(b) Simultaneous measurement of vibrissa position (blue) and breathing (red). Protraction and inspiration are upward.
(c) Histogram of instantaneous breathing frequencies (top) delineates the classification of breaths below 3 Hz as basal respiration and those above 5 Hz as sniffs. The spectral power of whisking (bottom) is plotted during periods of basal respiration (black) as well as sniffing (red).
(d) Rasters of inspiration onset times (red) and protraction onset times (blue) relative to the onset of inspiration for individual breaths are ordered by the duration of the breath; green arrow represents the 30 ms lead of inspiratory drive to facial muscles as opposed to the measured inspiration. Whisks and inspiration onset times are significantly correlated during both sniffing and basal respiration (p < 0.01).