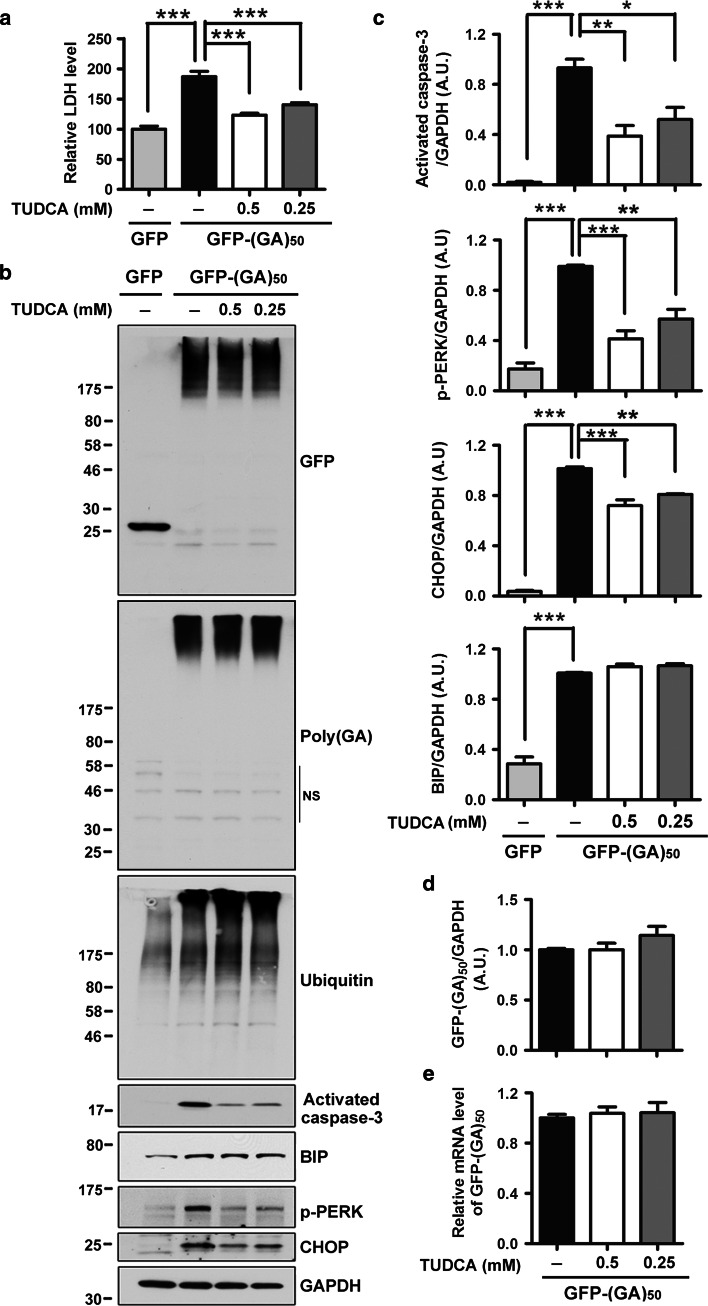
Fig. 5.
The chemical chaperone TUDCA protects neurons against poly(GA)-induced ER stress and toxicity. a TUDCA, a chemical chaperone known to inhibit ER stress and associated downstream pathways, significantly decreases LDH activity in media of neurons expressing GFP-(GA)50. b, c Treatment of GFP-(GA)50-expressing neurons with TUDCA also significantly inhibits caspase-3 activation, and decreases levels of ER stress markers, phospho-PERK and CHOP, as shown by Western blot (b) and densitometric analysis of blots (c). Note that TUDCA treatment does not decrease levels of ubiquitinated proteins and BIP (b, c). Protein and mRNA levels of GFP-(GA)50 are not changed after TUDCA treatment (d, e). NS non-specific bands. Data represents mean ± SEM from three separate experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, as analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis