Fig. 3.
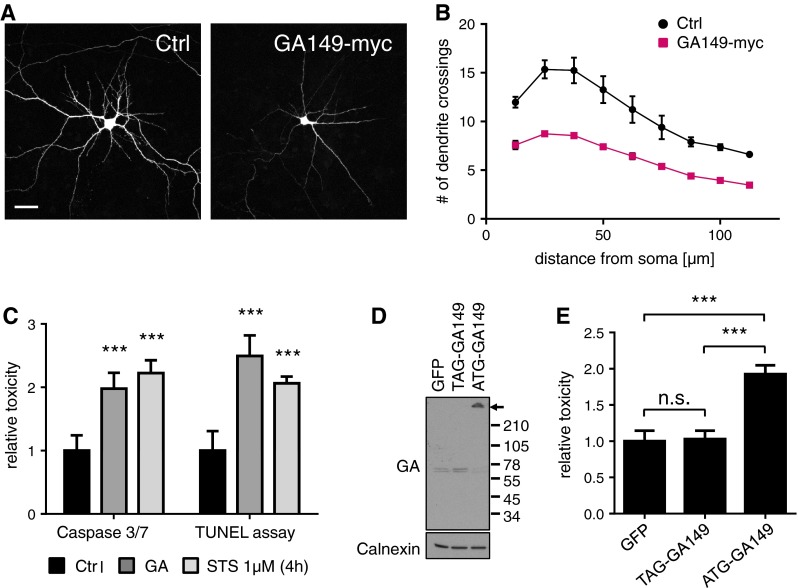
Poly-GA causes dendrite loss and induces apoptosis in primary neurons. a Cortical neurons were co-transfected with empty vector as control (Ctrl) or GA149-myc together with GFP to outline cell morphology (DIV7 + 4). Scale bars represent 40 µm. b Dendritic complexity was measured using Sholl analysis by manually counting the number of dendrites crossing concentric circles around the soma. Poly-GA expression leads to significant reduction of dendritic branching. N = 3 with 40 cells analyzed per condition in each experiment, mean ± SEM. p < 0.001 for 12.5 µm radius, p < 0.0001 from 25 to 50 µm radius, p < 0.001 for 62.5 µm radius, p < 0.01 for 75 µm radius and p < 0.05 from 87.5 to 112.5 µm radius (two-way ANOVA). c Apoptosis in transduced neurons was analyzed using a fluorogenic assay to detect caspase 3/7 activation and a TUNEL assay to detect apoptotic DNA fragmentation (DIV6 + 17). Caspase 3/7 activity was increased 2.0-fold in GA149-myc transduced cortical neurons. TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells (manually counted using the Fiji cell count plug-in) were increased by 2.5-fold in GA149-myc transduced hippocampal neurons compared to control cells. Representative images of TUNEL stainings are shown in Fig. S2. DIV6 + 17. n = 3 experiments with 6 replicates each; mean ± SD, Student’s t test, ***p < 0.001. d Immunoblots of cortical neurons transduced with GA149-myc constructs with or without start codon (DIV8 + 10). Replacing the ATG start codon in the synthetic GA149-myc gene with a TAG stop codon prevents poly-GA expression and aggregation. Arrow indicates top of the gel. e LDH release assay detected neurotoxicity of GA149-myc only in the presence of an ATG start codon in transduced cortical neurons (DIV8 + 14). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. ***p < 0.001, n = 3 with six replicates in each experiment
