Fig. 1. Subtypes of glutamatergic excitatory and GABAergic inhibitory and their laminar distribution within the neocortex.
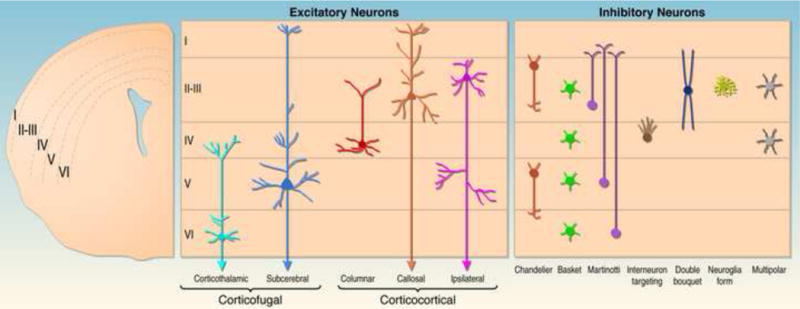
On the right a coronal hemisection of the brain is shown. Neocortical cell layers I–VI are indicated. The middle panel shows the position of major subtypes of excitatory neurons within neocortical cell layers and their projection pattern. Note that the diagram is a simplification outlining the major laminar distribution of neuronal subtypes. For example, the majority of callosal projection neurons is located in layers II and III, but a significant subset is also found in deeper layers. The left panel shows the position of several subtypes of inhibitory interneurons within neocortical cell layers.
