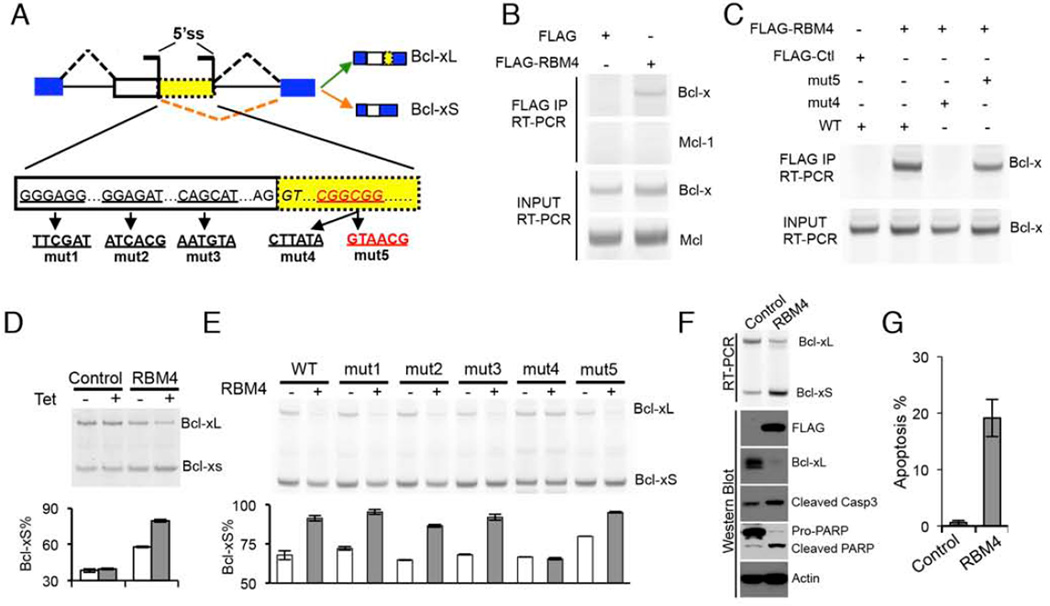
Figure 4. RBM4 regulates Bcl-x splicing to induce apoptosis.
(A) The schematic of Bcl-x pre-mRNA where the potential RBM4-binding site in red. Bcl-x splicing reporters with the indicated mutations (mut1 to 5) were generated. (B) Binding of Bcl-x pre-mRNAs with RBM4 is detected by RNA-immunoprecipitation assay in cells exogenously expression FLAG-RBM4 or vector control. The binding of Mcl-1 mRNA was used as specificity control. (C) 293 cells were co-transfected with Flag-RBM4 or vector control and the indicated mutant or wild-type (WT) Bcl-x reporters, and then immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody. The co-precipitated RNAs were detected by RT-PCR. (D) 293 cells containing tetracycline-inducible RBM4 or vector control were used to measure Bcl-x splicing. Increased levels of Bcl-xS in uninduced cells are likely due to expression leakage. The mean +/− SD of PSI from triplicate experiments were plotted. (E) Bcl-x splicing reporters containing various mutations were co-expressed with RBM4 or vector control in 293T cells to assay for the splicing change of Bcl-x. The mean +/− SD of Bcl-xS% was plotted. A representative gel from triplicate experiments was shown. (F) H157 cells expressing RBM4 or vector control were used to examine apoptotic markers including Bcl-xL, cleaved caspase 3 and PARP. (G) Expression of RBM4 promotes apoptosis. H157 cells expressing RBM4 or control were stained with propidium iodide and the apoptotic cells were detected by flow cytometry. The mean +/− SD of percentage of apoptotic cells from triplicate experiments were plotted. See also Figure S4.