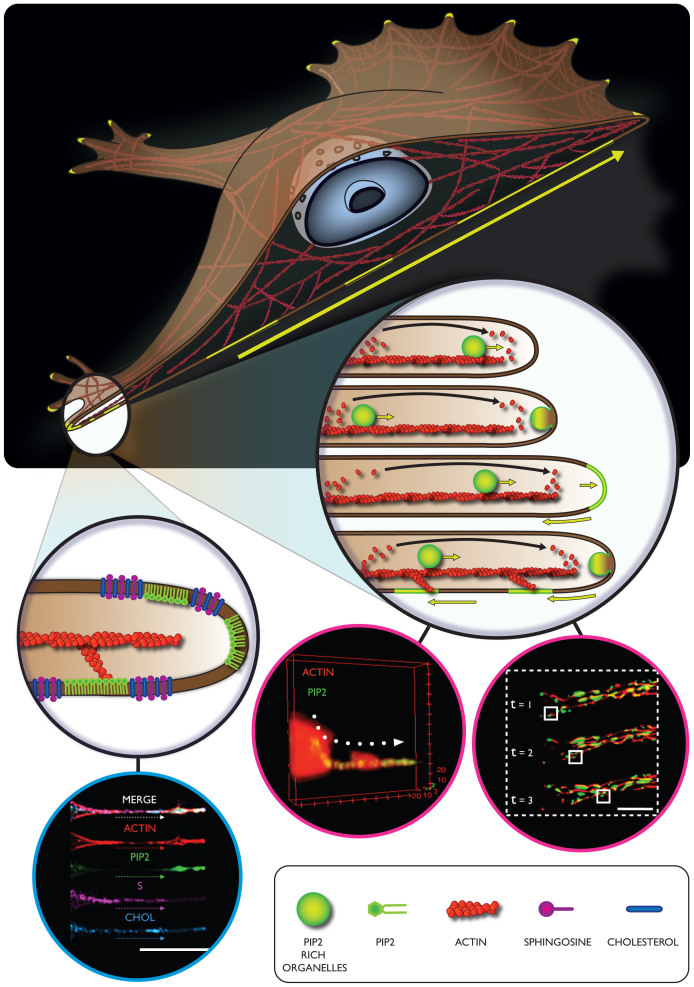
Figure 5. Schematic of a proposed mechanism involving different cellular components during important processes such as adhesion and spreading.
In the proposed mechanism, PIP2 has the central role to coordinate the actin polymerization and the formation of membrane adhesion domains. Furthermore we are showing a PIP2 rich organelles transport alongside the F-actin structures that possibly serve as membrane reservoir and finally culminate in cell protrusion elongation. Finally we are proposing sphingosine and cholesterol as important membrane constituents for the conformational stabilization of tubular cell fibers.