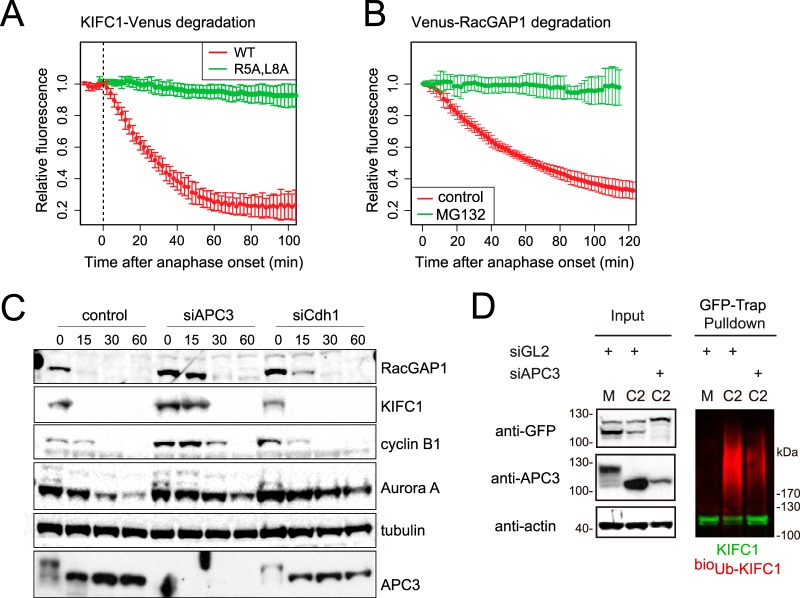
Fig. 4.
KIFC1 and RacGAP1 are mitotic exit-specific APC/C substrates. A–B, Venus-tagged KIFC1 or RacGAP1 were electroporated into U2OS cells, and after 12 to 24 h mitotic cells were imaged by means of fluorescence time-lapse microscopy. Venus levels in individual mitotic cells were quantified and plotted as a function of anaphase onset. In vivo degradation curves are shown as averaged results with error bars showing standard deviations. A, KIFC1-Venus is a substrate of mitotic-exit-specific proteolysis that depends on a putative D-box (R5xxL) in the unstructured N terminus. B, Venus-RacGAP1 is a substrate of mitotic-exit-specific proteolysis, as a decrease in Venus-RacGAP1 levels did not occur in cells treated at anaphase onset with 5 μm MG132. See also supplemental Fig. S4. C, depletion of APC3 stabilizes endogenous KIFC1 and RacGAP1 in mitotic exit. U2OS cells were transfected with siRNA against control (luciferase, GL2), APC3, or Cdh1 sequences, synchronized to prometaphase as described in Fig. 1D and released using CDKI/II inhibitor. Cells were harvested at the indicated time points, and whole cell lysate was examined via immunoblot with antibodies against known and putative APC/C substrates. APC3 immunoblot indicated progress of mitotic exit with reversal of marked mitotic phosphorylation shift. D, in vivo ubiquitination of KIFC1-Venus was sensitive to the depletion of APC3. KIFC1-Venus electroporated into bioUb cells synchronized in M and C phases as in C was subjected to GFP-Trap® pulldown as described in Ref. 57. Anti-GFP immunoblot revealed unmodified KIFC1-Venus (in green), whereas anti-biotin immunoblot revealed KIFC1-Venus-associated ubiquitin conjugates (in red).