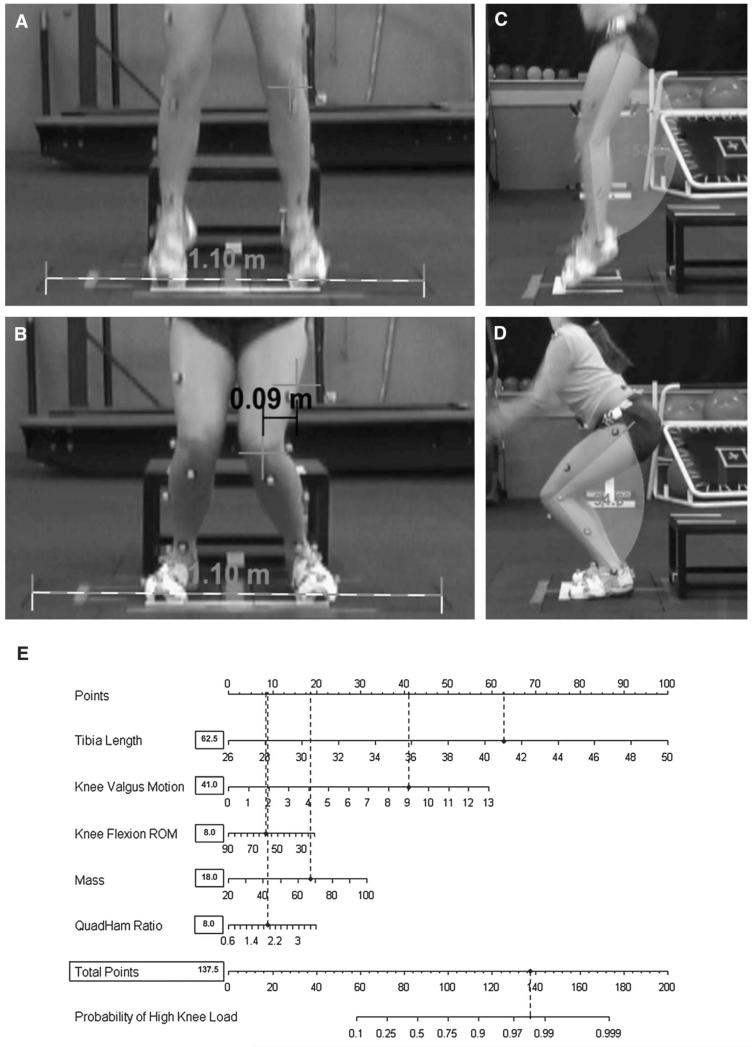
Figure 4.
Example of representative subject with excessive knee valgus during the drop vertical jump that contributes to her increased risk to demonstrate high KAM landing mechanics. A and B) The calibrated displacement measure between the 2 marked knee coordinates is representative of knee valgus motion during the drop vertical jump. C and D). The displacement of knee flexion is calculated as the differences in knee flexion angles at the frame before initial contact and maximum knee flexion and is representative of knee flexion ROM. E) Completed algorithm for the representative subject (tibia length: 41.0 cm; knee valgus motion: 9.0 cm; knee flexion ROM: 59.8°; mass: 67.5 kg; QuadHam ratio: 1.90). Based on her demonstrated measurements, this subject would have a 98% (137.5 points) chance to demonstrate high KAM during the drop vertical jump. Her actual KAM measure for the presented drop vertical jump that was quantified simultaneously with three-dimensional motion analysis was 44.1 N m of knee abduction load.