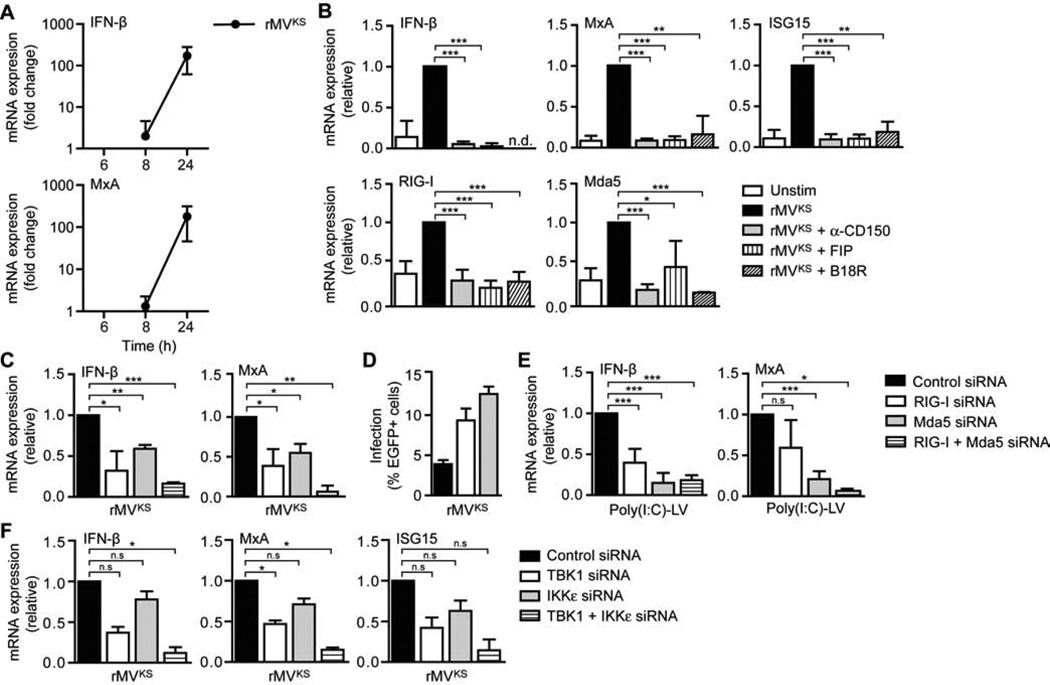
Figure 2. MV-induced type I IFN responses in DCs are dependent on RLR signaling via TBK1 and IKKε.
(A–C,E–F) IFN-β, MxA, ISG15, RIG-I, and Mda5 mRNA expression by DCs at indicated times (A) or 24 h after infection with rMVKS (B,C,F), or 8 h after stimulation with poly(I:C)-LyoVec (poly(I:C)-LV) (E), in the absence or presence of blocking CD150 antibodies, fusion inhibitor protein (FIP), or neutralizing soluble IFNAR (B18R) (B), or after silencing of RIG-I and/or Mda5 (C,E), or TBK1 and/or IKKε (F) by RNA interference (siRNA), measured by real-time PCR, normalized to GAPDH, and set at 1 in MV- or poly(I:C)-LV-stimulated (control-silenced) cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD. N.d., not determined; n.s., not statistically significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (Student's t-test).
(D) Infection of DCs 24 h after infection with rMVKS after silencing of RIG-I or Mda5, determined by flow cytometry by measuring % of EGFP+ cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD of duplicate samples.
Data are representative of at least four (A), three (B–E) or two (F) independent experiments. See also Figure S1.