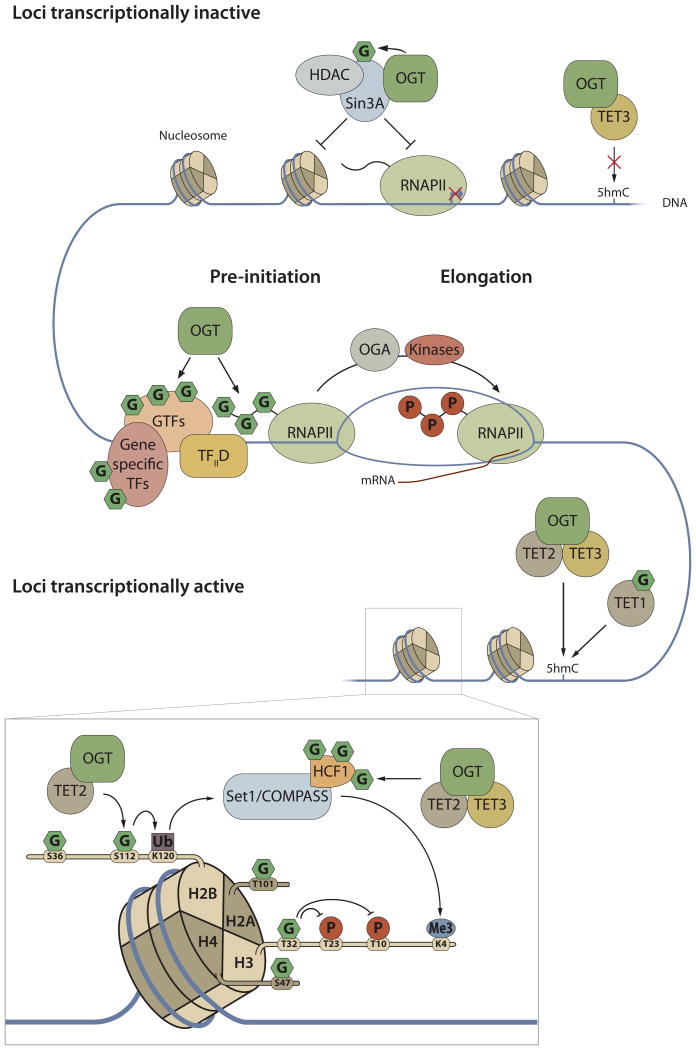
Figure 2. Regulation of gene transcription and epigenetics by O-GlcNAcylation.
O-GlcNAc cycling on gene specific transcription factors and components of the basal transcriptional machinery regulates gene activation. Sp1 is one of the most extensively modified transcription factors. The CTD of the RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) is itself O-GlcNAcylated at the transcription initiation step. The switch from transcription initiation to elongation requires OGA activity to remove the sugar. O-GlcNAcylation or OGT interaction with master regulators of epigenetic marks also switch on and off gene expression. The complex comprised of Sin3A, HDAC and OGT has been proposed to inhibit transcription. OGT O-GlcNAcylates and/or forms complexes with TETs that drive DNA methylation. H2B O-GlcNAcylation and ubiquitination are associated with transcriptionally active loci. Insert emphasizes the role of O-GlcNAcylation in the regulation of the histone code.