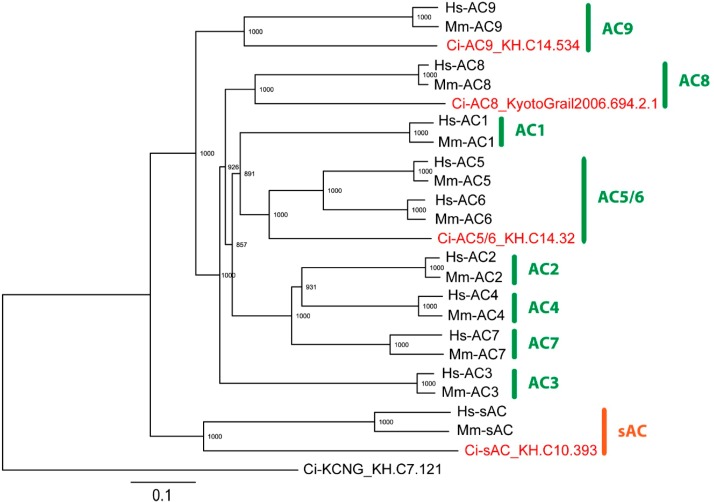
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of adenylyl cyclases. Ciona tetrameric potassium-selective cyclic nucleotide-gated channel (Ci-KCNG) was used as the outgroup. The value on each branch represents the number of times that a node was supported in 1000 bootstrap pseudo replications. BLASTP search of adenylyl cyclase (AC) against Ciona genome revealed four AC gene models. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that ACs encoded by these four genes are grouped with mammalian AC5/6, AC8, AC9 and soluble AC (sAC) respectively. Accession numbers of proteins are: Homo sapiens: Hs-AC1 (NP_066939), Hs-AC2 (NP_065433), Hs-AC3 (NP_004027), Hs-AC4 (NP_640340), Hs-AC5 (NP_899200), Hs-AC6 (NP_056085), Hs-AC7 (NP_001105), Hs-AC8 (NP_001106), Hs-AC9 (NP_001107), Hs-sAC (NP_060887); Mus musculus: Mm-AC1 (NP_033752), Mm-AC2 (NP_705762), Mm-AC3 (NP_001153008), Mm-AC4 (NP_536683), Mm-AC5 (NP_001012783), Mm-AC6 (EDL04180), Mm-AC7 (NP_001032813), Mm-AC8 (NP_033753), Mm-AC9 (NP_033754), Mm-sAC (NP_766617). Sequences of Ciona proteins are obtained from the Ghost database (http://ghost.zool.kyoto-u.ac.jp). Proteins encoded by Ciona gene models are indicated in red. The bars in green or in red represents tmAC or sAC, respectively.