Figure 2. Main cancer-related cell functions targeted by miRNA in lung cancer.
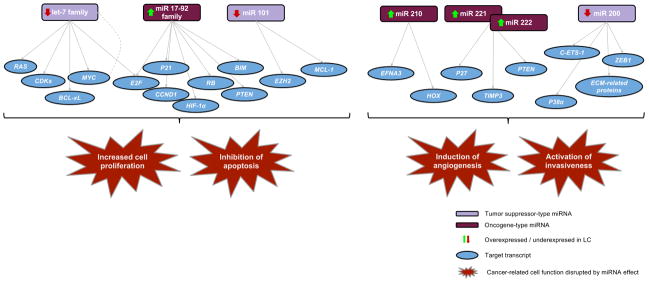
Multiple targets of lung cancer related key miRNAs are evidenced, as well as the variety of downstream effects. Members of the Let-7 and miR17-92 families are involved in disruption of cell cycle and apoptotic processes in lung cancer. The let-7 cluster negatively regulates multiple oncogenes, including Ras and Myc. Myc is thought to negatively regulate let-7 members by binding directly to their promoters (grey dotted line). Over-expression of miR-17-92 family and miR-101 contribute to cell survival by reducing apoptosis. On the other hand, miRNAs are involved in lung cancer progression (mainly through induction of angiogenesis and activation of invasiveness). This is the case of miR-221 and miR-222 that target PTEN and TIMP3 tumor suppressors and enhance cellular migration through activation of the Akt pathway and metallopeptidases; and miR- 210, which is involved in angiogenesis by targeting EFNA3 and the HOX family of transcription factors. The miR-200 cluster restricts metastasis and EMT by targeting E-cadherin transcriptional regulators such as ZEB proteins.
