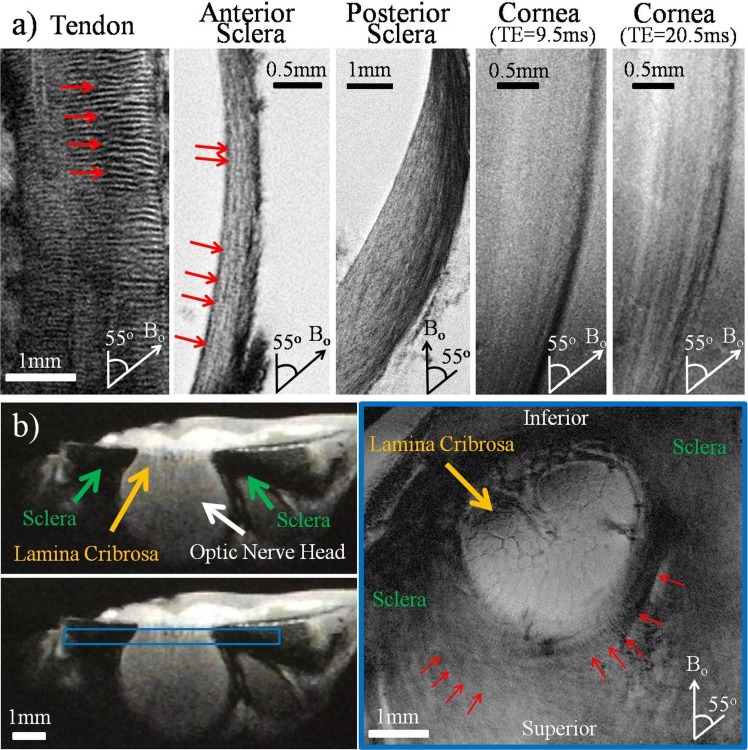
Figure 4.
(a) High-resolution T2*-weighted MR images of the normal unloaded tendon, anterior sclera, posterior sclera, and cornea positioned at the magic angle at approximately 55° to the main magnetic field (Bo). Collagen fiber crimps (red arrows) were observed in the tendon positive control and the anterior sclera. Lamellar fibers were observed along the anterior and posterior sclera, whereas differential image contrasts were found across corneal layers at echo times of 9.5 and 20.5 ms. Outer layers are to the right in the sclera and cornea images. Repetition time for all tissues = 3 s; echo time of tendon, anterior sclera, and posterior sclera = 8, 9.5, and 8 ms, respectively; in-plane resolution of tendon, anterior sclera, posterior sclera, and cornea = 20 × 20, 16 × 16, 20 × 20, and 16 × 16 μm2, respectively. (b) T2*-weighted MR images of the unloaded sclera near the optic nerve head. The left panels show the cross-section of the sclera, optic nerve head, and lamina cribrosa in sagittal view. The right panel shows the coronal T2*-weighted image oriented as the blue box in the left panel at 16 × 16 μm2 in-plane resolution and repetition time/echo time = 3000/9.5 ms. Details of the lamina cribrosa (yellow arrow) within the optic nerve head and the distributions of crimps (red arrows) in the scleral fibers surrounding the optic nerve head were revealed especially at orientations near the magic angle.