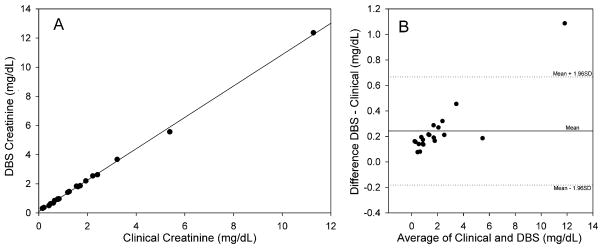
Fig. 2.
Panel A: Correlation between creatinine determined from a general patient population in the clinical laboratory and a DBS card. Blood samples were obtained from the clinical laboratory and DBS was prepared by spotting 30 μl as described in Methods. The creatinine values obtained in the clinical laboratory using the Jaffe method are plotted versus the levels obtained using LC–MS/MS from the DBS. The line is from linear regression analysis with slope = 1.077, intercept = 0.093, R2 = 0.999, P < 0.001, N = 20. Panel B: Bland–Altman relation showing the difference in creatinine concentrations from the data plotted in Panel A. The central horizontal line represents the mean difference or bias. The two other lines represent the expected distribution of 95% of the measured points as determined by the combined total variation of each individual method.