Figure 2. Molecular signature associated with IRF4 in hematological malignancies.
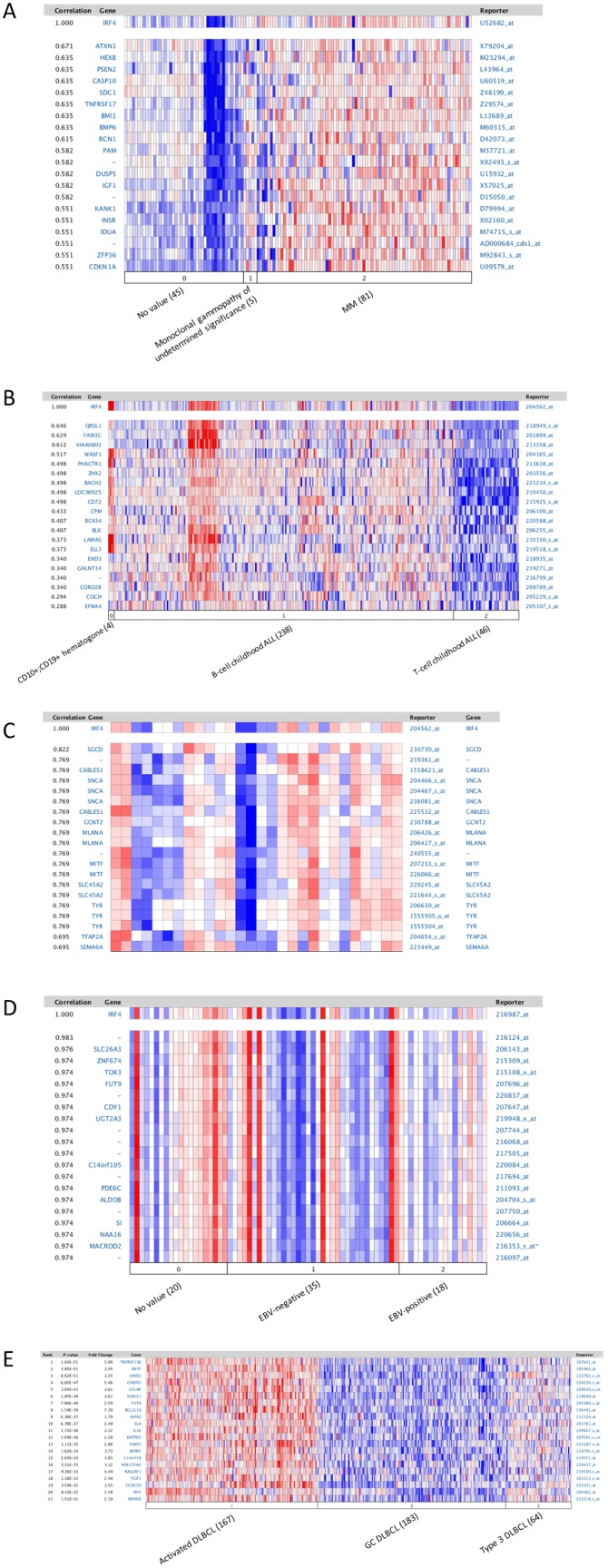
A. IRF4-associated gene expression pattern in myeloma. The dataset includes 131 samples [44]. Analysis was performed with default parameters (p value: 10−4, fold change: 2, and gene rank: top 10%). 0. No value (45 samples); 1. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (5 samples); 2. Multiple myeloma (81 samples including 74 clinical samples and 7 cell lines). B. IRF4-associated gene expression pattern in leukemia. The dataset includes 288 B- and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia samples [45]. 0. CD10+;CD19+ hematogone (4 samples); 1. B-Cell childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (238 samples); 2. T-cell childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (46 samples). C. IRF4-associated gene expression pattern in melanoma. The dataset includes 28 cutaneous melanoma patient samples [46]. D. IRF4-associated gene expression pattern in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. The dataset includes 64 Hodgkin’s lymphoma, 3 T-cell/histiocyte-rich B-cell lymphoma, 3 Hodgkin’s lymphoma cell lines, and 3 lymphadenitis samples (60 cHL samples in total) [48]. 0. No value (20 samples); 1. EBV negative (35 samples); 2. EBV positive (18 samples). E. The gene expression pattern correlated with IRF4 in non-Hodgkin lymphoma DLBCL. The dataset comprises 414 DLBCL samples [42]. 1. Activated B cell-like DLBCL (167 samples); 2. Germinal center B cell-like DLBCL (183 samples); 3. Type 3 DLBCL (64 samples).
