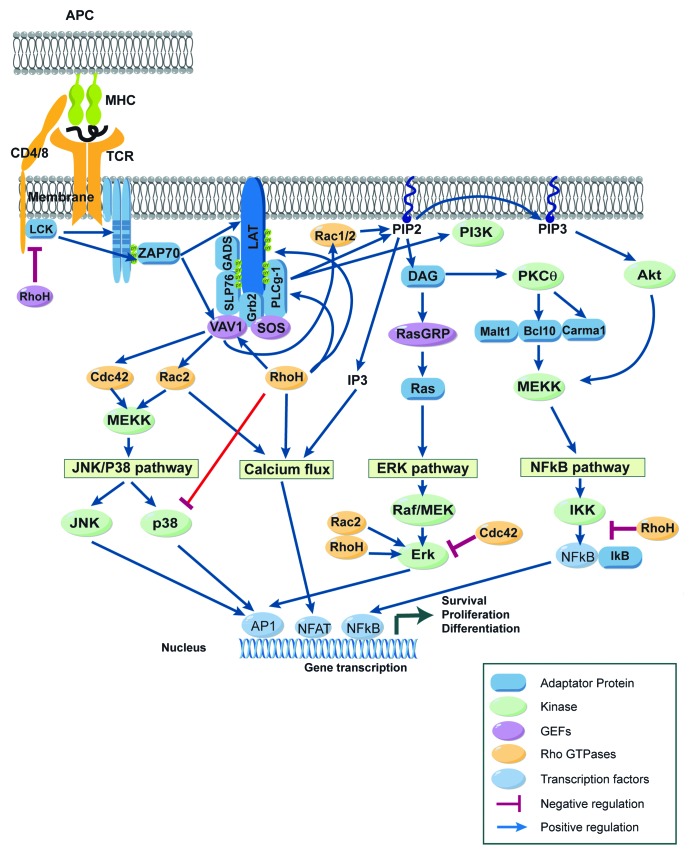
Figure 2. Rho-GTPases regulate signaling pathways induced after TCR engagement. Schematic view of the signaling events induced in mature T cells after the recognition of an antigen presenting cell (APC) expressing peptide-MHC complexes. Binding of the T-cell receptor (TCR) to its ligand leads to a complex cascade of biochemical events that initiate distinct signaling pathways including (1) the Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) pathway including extracellular signal–regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38, (2) the Ca/calcineurin/NFAT pathway, and (3) the NF-κB pathway. Eventually, these signaling pathways result in the activation of transcription factors like AP-1, NFAT, and NF-κB, which control the gene expression program characteristic of activated T cells. Rho-GTPases regulate positively (blue arrows) or negatively (red lines) these TCR signaling pathways. For more details, see text.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.