Table 1.
Effects of the light source and the ketone catalyst on the benzylic fluorination of 1 and 2
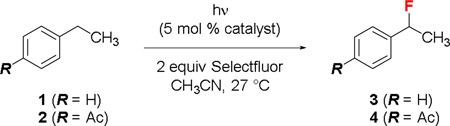 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Substrate | Catalyst | Light source | Time | Yield[i] |
| 1 | 1 | 9-fluorenone | 1 × CFL[a] | 24 h | 89% (85%)[j] |
| 2 | 1 | – | 1 × CFL[a] | 24 h | 0% |
| 3 | 2 | 9-fluorenone | 1 × CFL[a] | 24 h | 80% (76%)[j] |
| 4 | 2 | – | 1 × CFL[a] | 30 h | 89% |
| 5 | 2 | – | 16 × RPR-3000Å[b] | 30 min | 46% |
| 6 | 2 | – | 16 × RPR-3500Å[c] | 1 h | 73% |
| 7 | 2 | – | 16 × RPR-4190Å[d] | 6 h | 96% |
| 8 | 1 | acetophenone | 16 × RPR-4190Å[d] | 6 h | 88% |
| 9 | 1 | acetophenone | 16 × RPR-4190Å[d,e] | 20 h | 70% |
| 10 | 1 | acetophenone | 16 × RPR-4190Å[d,f] | 20 h | 0% |
| 11 | 1 | acetophenone | 1 × violet LED[g] | 3 h | 85% |
| 12 | 1 | acetophenone | 1 × CFL[a] | 20 h | 61% |
| 13 | 1 | acetophenone | 1 × CFL[a,e] | 20 h | 50% |
| 14 | 1 | acetophenone | 1 × CFL[a,f] | 20 h | 0% |
| 15 | 1 | acetone | 1 × CFL[a} | 20 h | 0% |
| 16 | 1 | acetophenone | –[h] | 24 h | 0% |
19 W, household lamp.
21 W, 250–375 nm.
24 W, 300–420 nm.
375–465 nm.
With a 375 nm longpass filter.
With a 400 nm logpass fileter.
9 W, 370–405 nm.
50 °C.
Determined by 19F NMR using C6H5F as an external standard.
Isolated yield.
