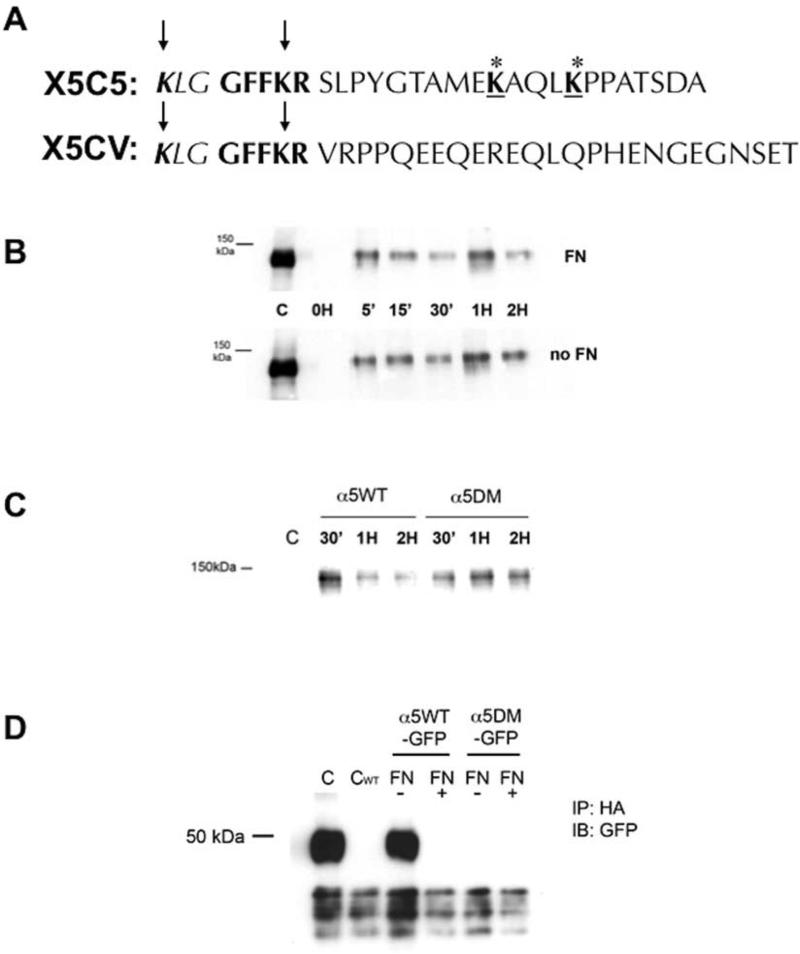
FIGURE 3. α5 integrin degradation in the absence of fibronectin requires the cytoplasmic tail of α5 integrin distal to the conserved GFFKR region and containing two lysine residues that are ubiquitinated.
(A): A chimeric integrin construct was constructed where the α5 cytoplasmic tail of the α5 integrin distal to the GFFKR amino acid sequence was replaced with the αV cytoplasmic tail (X5CV). CHO cells were bulk transfected to stably express the chimeric α5 integrin (X5CV cells) at expression levels comparable to wild-type cells (X5C5 cells). (B): Retention of internalized α5 integrin in X5CV cells was analyzed at indicated times as described in Fig. 1. Internalized X5CV receptor was not degraded in the absence of FN (Panel B) as had been observed with the wild-type receptor (Fig. 1A). (C): Site-directed mutagenesis was performed to obtain a double mutant construct (α5DM) in which the lysines at positions 1038 and 1042 in the cytoplasmic tail of α5 integrin, distal to the conserved GFFKR region, were replaced with alanine residues. α5-null CHO cells were bulk transfected to stably express the α5DM integrin at expression levels comparable to wild-type cells (α5WT cells). Cells (α5WT and α5DM) were then cultured overnight in the absence of FN. Retention of internalized α5WT and α5DM integrin was analyzed at indicated times as described in Fig. 1. α5DM integrin was readily detected at two hours, in contrast to the α5WT integrin which was significantly reduced. (D): CHO cells stably expressing α5WT or α5DM integrin with a C-terminal GFP-tag (α5WT-GFP and α5DM-GFP, respectively) were transiently transfected with an HA-tagged ubiquitin cDNA and cultured overnight in the presence or absence of FN, followed by pretreatment with MG-132 for one hour. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA monoclonal antibody followed by immunoblotting with an anti-GFP antibody to detect GFP-labeled α5 integrin cytoplasmic domain (~50 kDa; see also Figure 4 and text). Whole cell lysates of α5WTGFP (C) or α5WT (CWT) served as control. Loss of the two carboxyl-terminal lysine residues in the cytoplasmic tail of α5 integrin resulted in loss of the ability of that region to be ubiquitinated in the absence of FN.