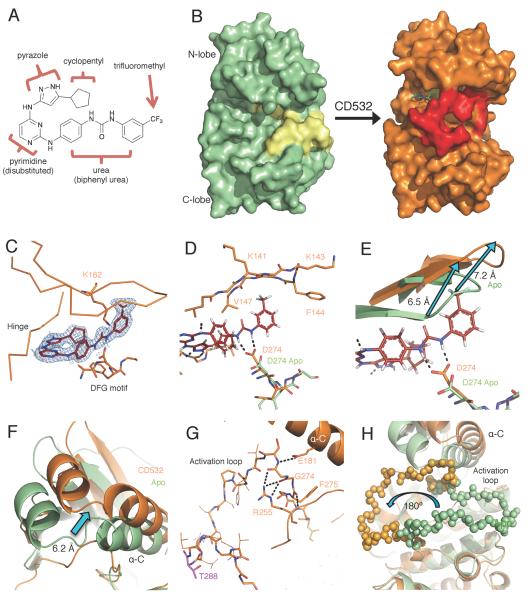
Figure 3.
CD532 stabilizes an inactive, DFG-in conformation of Aurora A. (A) The structure of CD532 with key components highlighted. (B) Surface representations of Aurora A Apo (green, activation loop in yellow) and of Aurora A bound to CD532 (orange, activation loop in red). (C) CD532 (red sticks) in ATP binding pocket, overlaid with electron density before ligand fitting (blue mesh). (D) Interactions between CD532 (red), the DFG motif (D274) and β1/β2 (K141-V147) (E) Displacement of glycine rich loop in drug-bound structure (orange) as compared to Apo (green) due to drug binding. (F) Displacement of α-C helix of N-terminal domain allows for (G) a network of polar contacts between E181, R255, and DFG motif. (H) Stabilization of inactive orientation of the activation loop (activation loop in balls). Structural comparisons are all C-terminal alignments. See also Movie S1 and Table S1.