Figure 4.
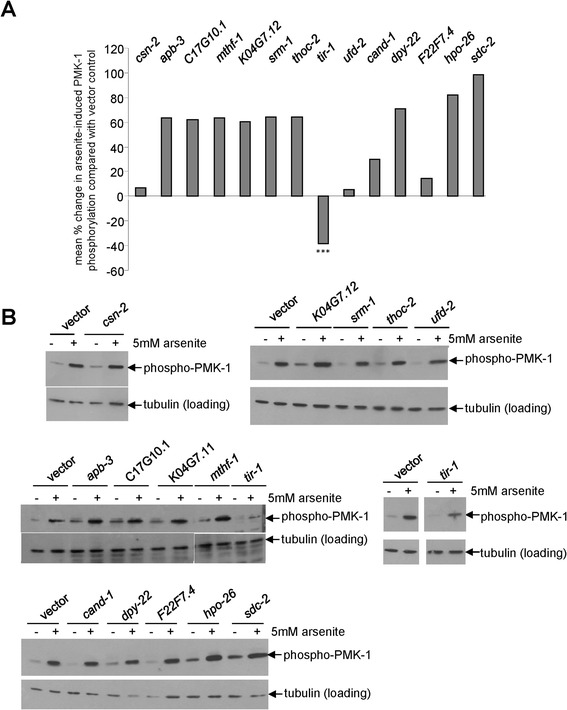
Effect of genes required for stress-induced activation of gcs-1 on arsenite-induced PMK-1 activation. Western blot analysis of RNAi and vector-control-treated animals before and following 5 min exposure to 5 mM arsenite revealed that out of 14 of the most robust activators of gcs-1p::gfp (Table 1), only tir-1 RNAi reduced the level of PMK-1 phosphorylation. (A) Mean percentage difference between the level of PMK-1 phosphorylation in arsenite-treated control and RNAi-treated animals following analysis of quantitative densitometry data obtained from at least two independent experiments. ***indicates that tir-1 RNAi significantly reduced PMK-1 phosphorylation compared with vector control (Student’s T test, P = 0.00056). The effects of other RNAi clones on arsenite-induced PMK-1 phosphorylation were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). (B) Representative Western blots of those quantitatively analysed in (A). RNAi, RNA interference.
