Figure 3.
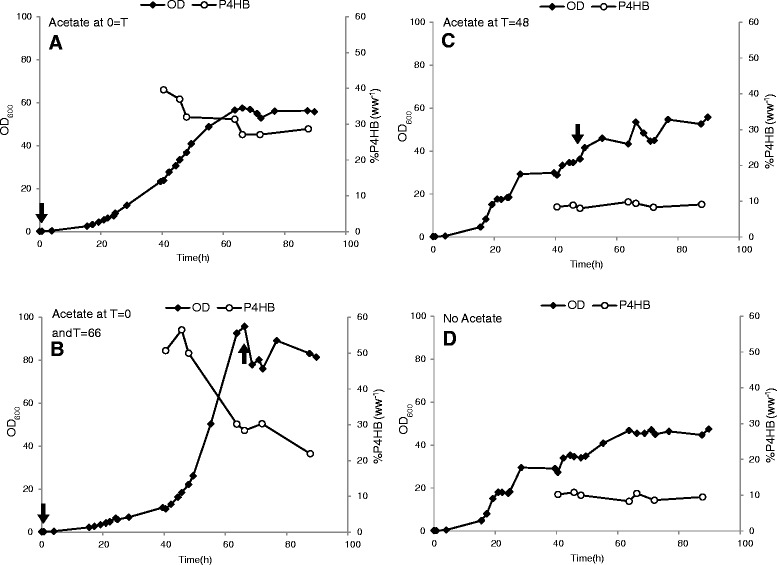
Fed-batch strategy using acetic acid as stimulator for P4HB synthesis in E . coli JM109 (pKSSE5.3) grown on modified M9 medium supplemented with 20 g L −1 glycerol, 6 g L −1 Na-4HB, 0.5 g L −1 NZ-amine, 0.015 g L −1 thiamine and 100 mg L −1 ampicillin. Acetic acid was added at different physiological states. For all cultures pulse-feeding started at 40 h of cultivation: T = 40.5 h, addition of 12 g L−1 glycerol and 6 g L−1 Na-4HB; T = 45.75 h, addition of 20 g L−1 glycerol; T = 63.75 h, addition of 10 g L−1 glycerol and 3 g L−1 Na-4HB; T = 72.25 h, addition of 20 g L−1 glycerol and 6 g L−1 Na-4HB; T = 76.75 h, addition of 10 g L−1 glycerol. Culture A, addition of 2 g L−1 acetic acid at the beginning of the cultivation; Culture B, addition of 1 g L−1 acetic acid at beginning and at the end of growth phase (66 h), respectively; Culture C, addition of 2 g L−1 acetic acid after 48 h cultivation; Culture D, no addition of acetic acid to the culture. Arrows represent the addition of acetic acid. The data are the average numbers of duplicates.
