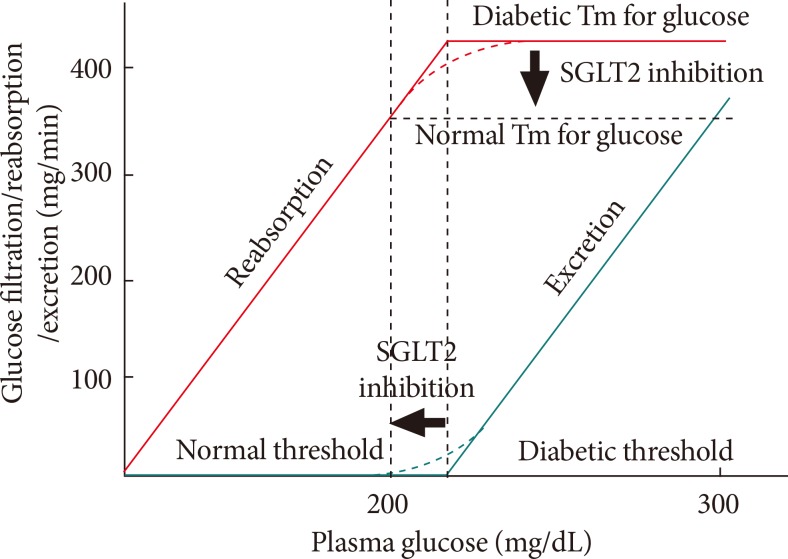
Fig. 2.
Renal glucose handling before and after sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibition. SGLT2 inhibition reduces the maximum transport rate (Tm) of glucose. This reduced Tm for glucose through SGLT2 inhibition results in a decrease in glucose reabsorption in the renal proximal tubule and lowers the renal threshold so that glucosuria occurs at a lower plasma glucose concentration.