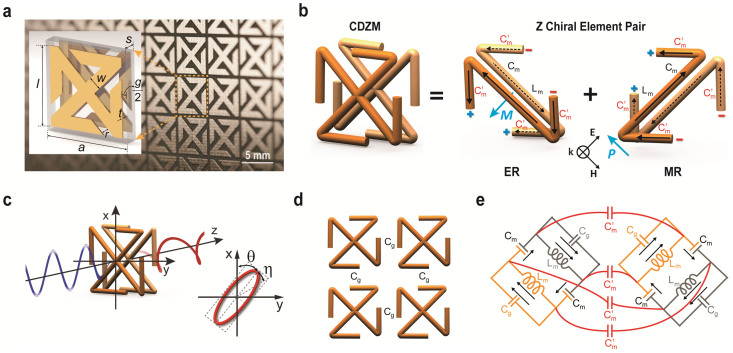
Figure 1.
Conjugated double Z metamaterial and an equivalent RLC model (a) Schematic view of the unit cell structure and photograph of the CDZM sample with the dimensions indicated in the figure: l = 5.5 mm, w = 0.9 mm, s = 0.5 mm, r = 0.6 mm, and the thickness of the copper t = 18 μm. The gap width between chiral metamolecules is defined by g = a – l. (b) Schematics of the equivalent RLC model for the CDZM. 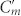 is the capacitances of the side strips and Lm and Cm are the inductance and capacitance of the central strips respectively. The incident electric field (E) induces the surface current in the central strip (black arrow) resulting in magnetization (M) and, similarly, the electric charges (represented by +, −) driven by the magnetic field (H) induces electric polarization (P). (c) Ellipticity angle η and azimuthal rotation angle θ represent the polarization state of the transmitted electromagnetic waves. (d) Schematics of CDZM arrays. Cg is the gap capacitance which represents additional inter-molecular coupling between metallic strips in neighbouring unit cells. (e) Equivalent RLC circuits for Z chiral element pairs. For simplicity, the resistor elements have been omitted. The arrow indicates the current direction.
is the capacitances of the side strips and Lm and Cm are the inductance and capacitance of the central strips respectively. The incident electric field (E) induces the surface current in the central strip (black arrow) resulting in magnetization (M) and, similarly, the electric charges (represented by +, −) driven by the magnetic field (H) induces electric polarization (P). (c) Ellipticity angle η and azimuthal rotation angle θ represent the polarization state of the transmitted electromagnetic waves. (d) Schematics of CDZM arrays. Cg is the gap capacitance which represents additional inter-molecular coupling between metallic strips in neighbouring unit cells. (e) Equivalent RLC circuits for Z chiral element pairs. For simplicity, the resistor elements have been omitted. The arrow indicates the current direction.