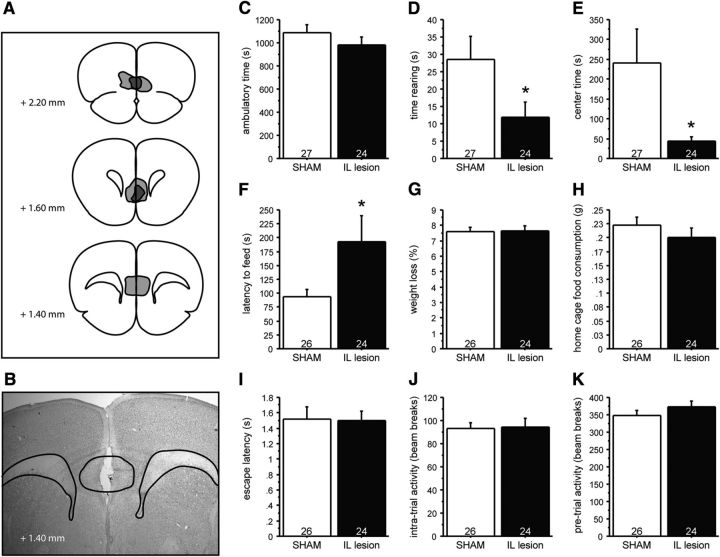
Figure 7.
IL lesions in control mice phenocopy the effects of PN-FLX treatment on anxiety-like behavior. Mice received bilateral injections in the IL using ibotenic acid (IL lesion) or saline solution (SHAM). A, B, Lesion extent was assessed histologically after behavioral experiments were concluded, with light gray demarcating the additive area lesioned, and dark gray demarcating the largest common area lesioned. C–E, Although IL lesions do not alter ambulatory time in the OF test (C), they significantly reduce the time spent rearing (D) and the time spent in the more anxiogenic center region (E) relative to SHAM lesioned controls. F–H, In the NSF test, IL lesioned mice take significantly longer to approach the food pellet relative to PN-VEH mice (F), while the percentage of weight loss after 24 h of food deprivation (G) and home-cage food consumption (H) are comparable. I–K, IL lesions did not significantly affect latency to escape (I), intratrial activity (J), or baseline pretrial activity (K) in the shock escape test. N values are indicated in the figure. *p < 0.05.