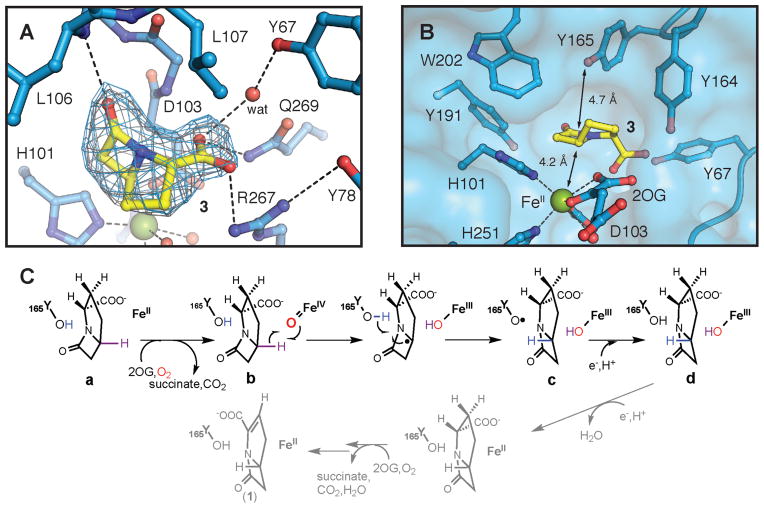
Figure 2.
Structure of the active site in the CarC•Fe(II) •2OG•3 complex and the mechanism of stereoinversion indicated by the structure and biophysical results presented in this study. (A) 2Fo-Fc (gray mesh, 1.2σ) and Fo-Fc omit (blue mesh, 2.6σ) electron density maps for 3 (carbon atoms shown in yellow). Dashed lines illustrate hydrogen-bonding interactions involving the substrate or bonds between the Fe(II) cofactor and its ligands. (B) Surface representation of the substrate-binding pocket showing the locations of nearby aromatic amino acids including Y165, the H• donor. Black lines indicate the distances between C5 of 3 and the Fe(II) or the hydroxyl substituent on Y165. Selected amino acid side chains, 2OG, and substrate 3 are shown in stick format. The Fe(II) ion and water molecules are shown as green and red spheres, respectively. (C) Mechanism of the CarC-mediated, stoichiometric stereoinversion of 3 to 4, involving abstraction of H• from C5 by a ferryl complex and H• donation by Y165.