Figure 3.
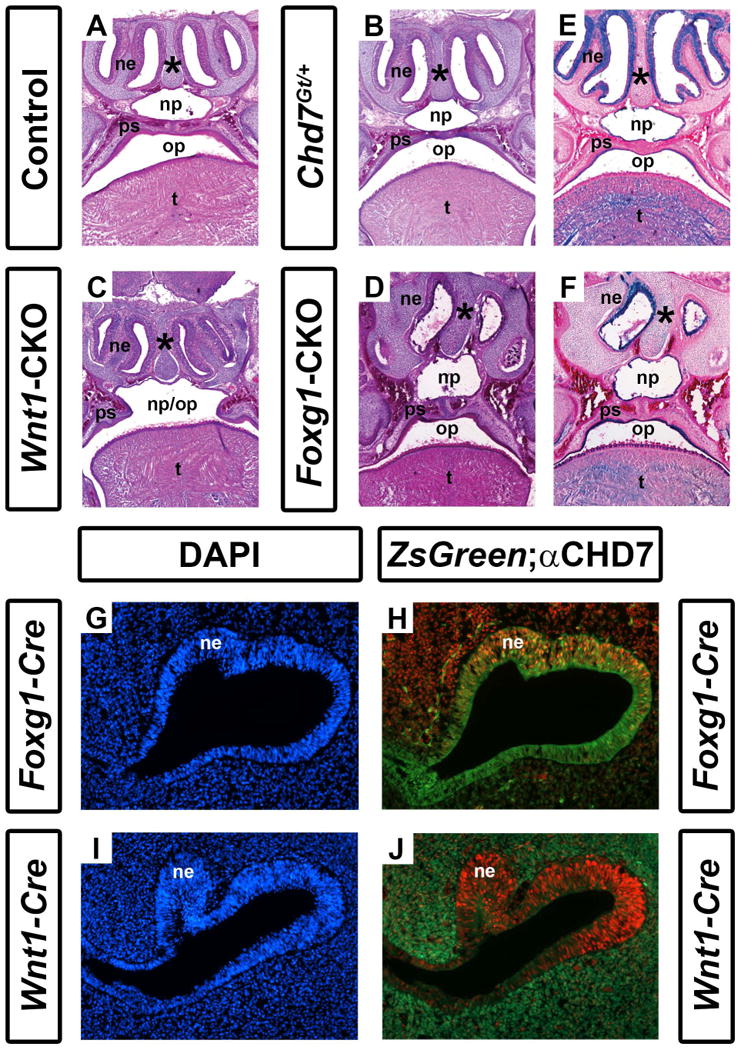
Conditional Chd7 deletion results in palatal and nasal epithelial dysplasia. Transverse sections of postnatal day 1 control (Cre-negative, Chd7+/f or Chd7f/f) (A), Chd7Gt/+ (B), Wnt1-CKO (C), and Foxg1-CKO (D) mice stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Control (A) and Chd7Gt/+ (B) mice exhibit fully fused palatal shelves (ps) with separation of the nasopharynx (np) from the oropharynx (op), whereas Wnt1-CKO(C) mice have severely hypoplastic palatal shelves (ps) resulting in a cleft palate and single pharyngeal cavity (np/op). Foxg1-CKO mice (D) have fused palatal shelves (ps) resulting in a highly-arched, intact palate , a thickened nasal septum (asterisk), and severely hypoplastic nasal epithelia (ne). (E) and (F) show X-gal/eosin stained sections of postnatal day 1 Chd7Gt mice, which express β-galactosidase under the control of the Chd7 promoter. X-gal staining is present in the nasal epithelium (ne), tongue (t) and epithelial cells lining the palatal shelves and combined oral-nasal pharynx (op/np) of Chd7Gt/flox (E) and Foxg1-CKO (F) mice. Panels (G-J) are transverse sections of Foxg1-Cre;ZsGreen (G, H) or Wnt1-Cre;ZsGreen (I, J) E11.5 embryos stained with DAPI (blue, marking cellular nuclei) or anti-CHD7 (red). Green fluorescence (ZsGreen reporter) marks Cre expressing cells and is overlaid with anti-CHD7 (red) in (H) and (J). Foxg1-Cre and Chd7 are both highly expressed in the developing nasal epithelium (ne) while Wnt1-Cre expression is restricted to the surrounding nasal mesenchyme (m) and is absent from the nasal epithelium proper.
