Figure 4.
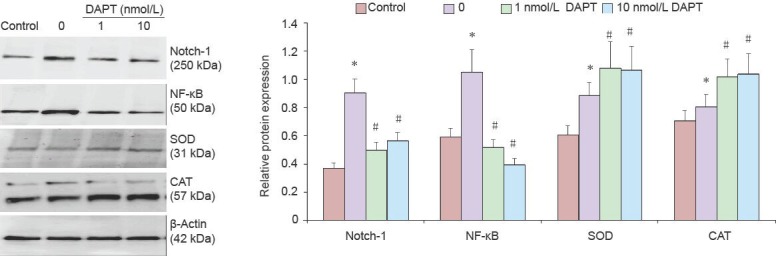
Role of Notch-1 signaling on cellular redox regulation after amyloid beta-peptide (25–35) (Aβ25–35) treatment.
The protein level of Notch-1, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) were detected by western blot assay. Values presented are absorbance ratios of Notch-1, NF-κB, SOD, and CAT to β-actin, which was used as an equal protein loading marker. Results are presented as mean ± SD (n = 5). Statistical analysis was performed by two sample independent t-test for comparison between two groups. All experiments were repeated at least three times. *P < 0.05, vs. control group; #P < 0.05, vs. model group (0). DAPT: N-[N-(3,5-Difluorophenacetyl)-L-alanyl]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl ester.
