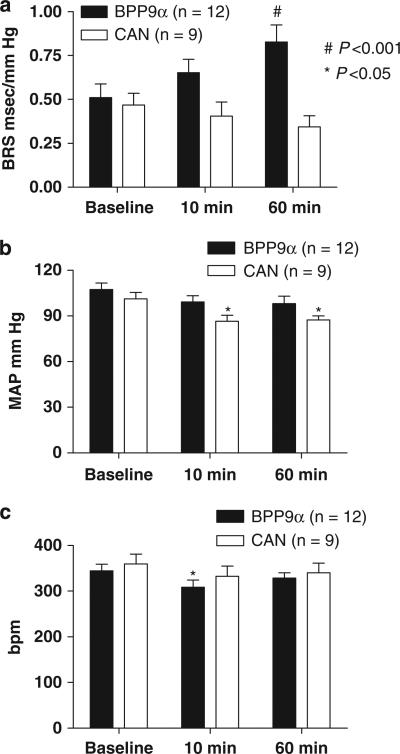
Figure 1.
The time course of changes in mean arterial pressure (MAP) and baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) after solitary tract nucleus (nTS) microinjection of AT1 receptor blocker, candesartan (CAN), or the peptidic angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, BPP9α, in male (mRen2)27 rats. (a) BRS for control of heart rate, (b) MAP and (c): heart rate (HR). CAN microinjected bilaterally into the nTS had no significant effect on BRS at 60 min after the microinjection. On the other hand, bradykinin potentiating nonapeptide, (BPP9α) microinjected bilaterally into the nTS improved BRS over time, requiring 60 min for the action to become significant. There was a significant lowering of MAP in the CAN but not BPP9α treatment group over this time frame. BPP9α significantly lowered HR at 10 min. *P<0.05 and #P<0.001 vs. baseline.