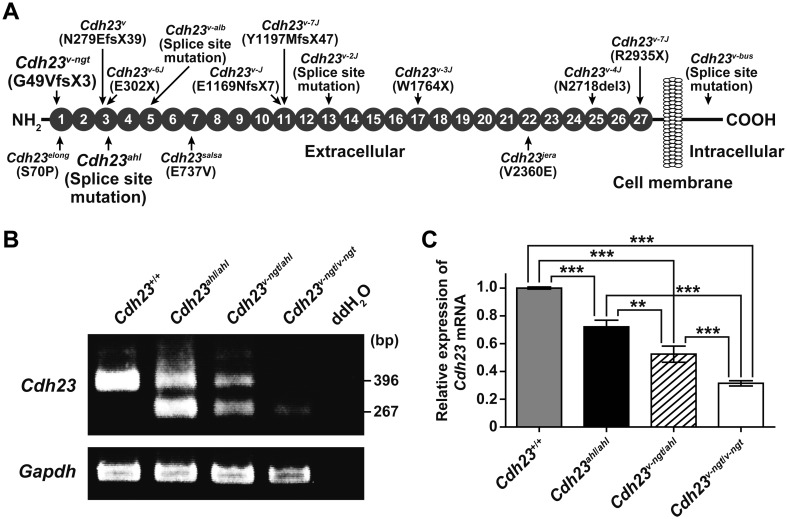
Fig. 1.
Cdh23 expression in hypomorphic Cdh23v-ngt/v-ngt homozygous, Cdh23v-ngt/ahl compound heterozygous, and null Cdh23v-ngt/v-ngt homozygous mice. (A) Schematic diagram of the CDH23 protein structure showing the locations (arrows) of the functionally null (top) and hypomorphic (bottom) mutations (modified from Manji et al. [13]). Gray circles indicate the extracellular cadherin repeats (ECs). (B) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of Cdh23 expression in the cochleae of Cdh23+/+, Cdh23ahl/ahl, Cdh23v-ngt/ahl, and Cdh23v-ngt/v-ngt mice at 1 month of age. The upper panel shows 396 bp and 267 bp RT-PCR products from Cdh23-specific primers located in exons 6 and 8, respectively. Smaller bands (129 bp), corresponding to transcripts in which exon 7 was skipped, were amplified in cDNA samples isolated from Cdh23753A mice. The integrity of the cDNA was confirmed using a Gapdh control band (bottom panel). (C) Relative levels of Cdh23 mRNA in the cochleae of Cdh23+/+, Cdh23ahl/ahl, Cdh23v-ngt/ahl, and Cdh23v-ngt/v-ngt mice at 1 month of age. Cdh23 mRNA expression was measured by real-time RT-PCR analysis using primer set D (Supplementary Table 1: refer to J-STAGE at https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/expanim). The expression levels in Cdh23+/+ mice were assigned an arbitrary value of 1 for comparative purposes. **P≤0.01 and ***P≤0.001.