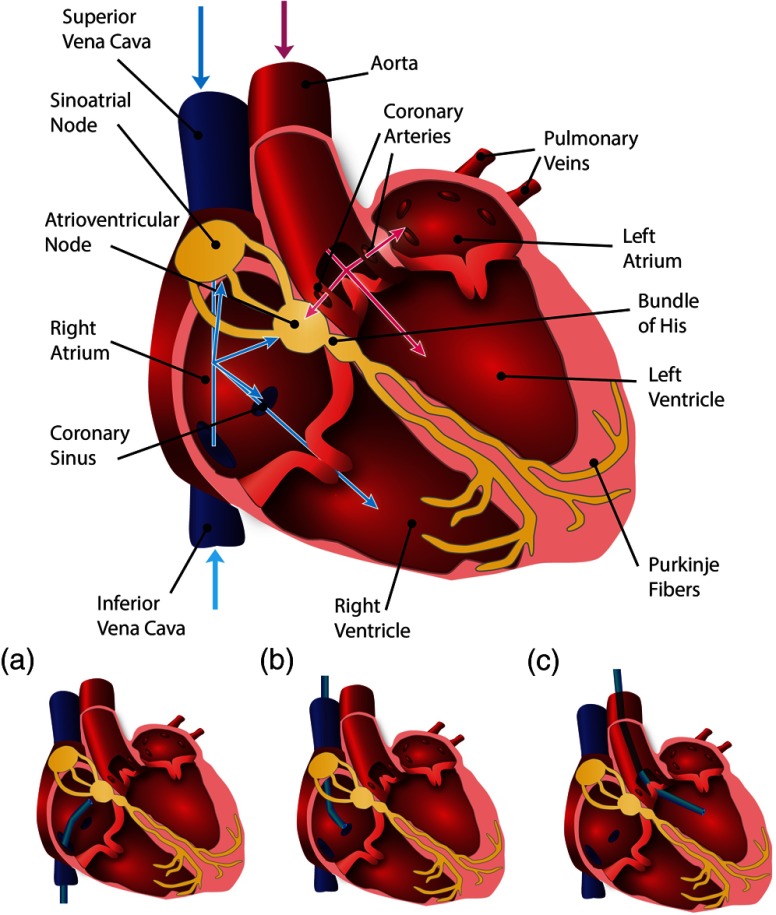
Fig. 4.
Schematic of endoscopic paths to access the electrical conduction system of the heart. Blue paths depict the access via the right side of the heart, where a catheter is inserted through the femoral vein to access the right atrium via the inferior vena cava (IVC) or through the brachial vein via the superior vena cava (SVC) (a and b). From the right atrium, the catheter can then access the atrioventricular (AV) node, sinoatrial (SA) node, and bundle of His, or be guided into the coronary sinus (CS) or right ventricle. Pink paths depict the access via the left side of the heart, where a catheter is inserted through the femoral artery in order to access the aorta (c); from there the SA node can be accessed via the coronary arteries or the catheter can be guided into the left ventricle.