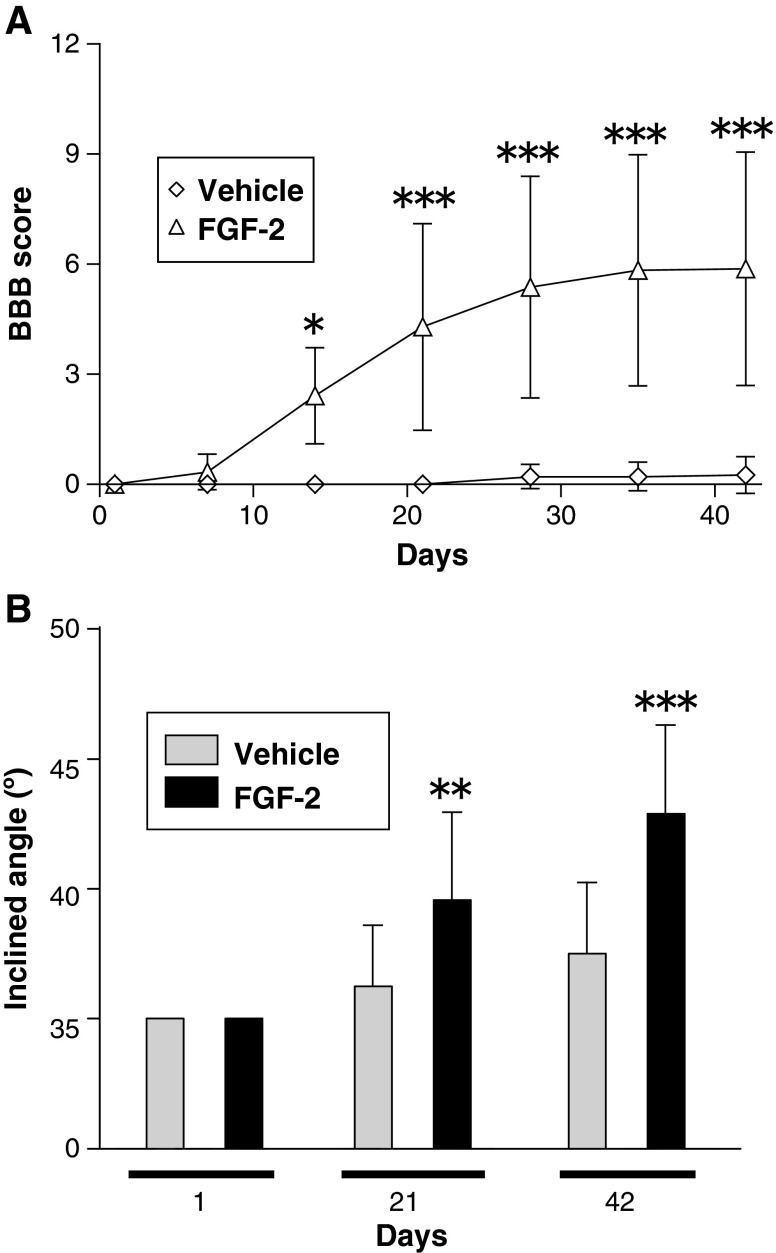
FIG. 1.
Fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) injection into the injured spinal cord improves locomotor function. (A) Time course of the locomotor function of the vehicle-treated (n=12) and FGF-2-treated animals (n=12) during the 6-week experimental period. The FGF-2-treated group showed a significant improvement over the vehicle-treated group. (B) Locomotor function was tested by use of the inclined plane test on the same groups of animals shown in A. Spinal cord injury caused locomotor loss in this test, but FGF-2 treatment ameliorated it. The FGF-2-treated rats could climb the board more steeply inclined than could the vehicle-treated rats (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 versus the vehicle-treated group; BBB, Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan locomotor scale).