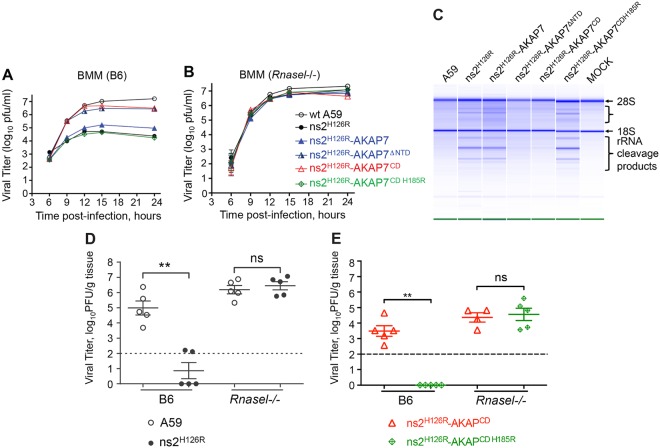
FIG 4 .
Expression of the N-terminal truncation or the CD of AKAP7 restores the replication of mutant ns2 in vitro and in vivo. Growth kinetics of chimeric AKAP7 viruses were determined on BMM from B6 mice (A) and Rnasel−/− mice (B). BMM were infected with each virus (as indicated) at an MOI of 1. Samples of the cultured supernatant were taken at the indicated time points, and viral titers were determined by plaque assays. The data are from one representative experiment of at least two, each performed in triplicate. (C) AKAP7 CD and N-terminally truncated proteins inhibit rRNA degradation during viral infection. B6 BMM were infected (MOI of 1) and harvested at 10 h postinfection, and the integrity of total cellular RNA was analyzed on RNA chips (Agilent). (D and E) Four-week-old B6 or Rnasel−/− mice were infected with 2,000 PFU/mouse intrahepatically with A59 and ns2H126R (D) or ns2H126R AKAP7CD and the double mutant ns2H126R AKAP7CD H185R (E). At day 5 postinfection, mice were sacrificed, and viral titers in the liver were determined by plaque assays. The dashed line represents the limit of detection, and error bars represent standard errors of means (n = 5). Asterisks indicate that differences are statistically significant (**, P < 0.05). Data are derived from one representative experiment of two. ns, not statistically significant.