FIG 2 .
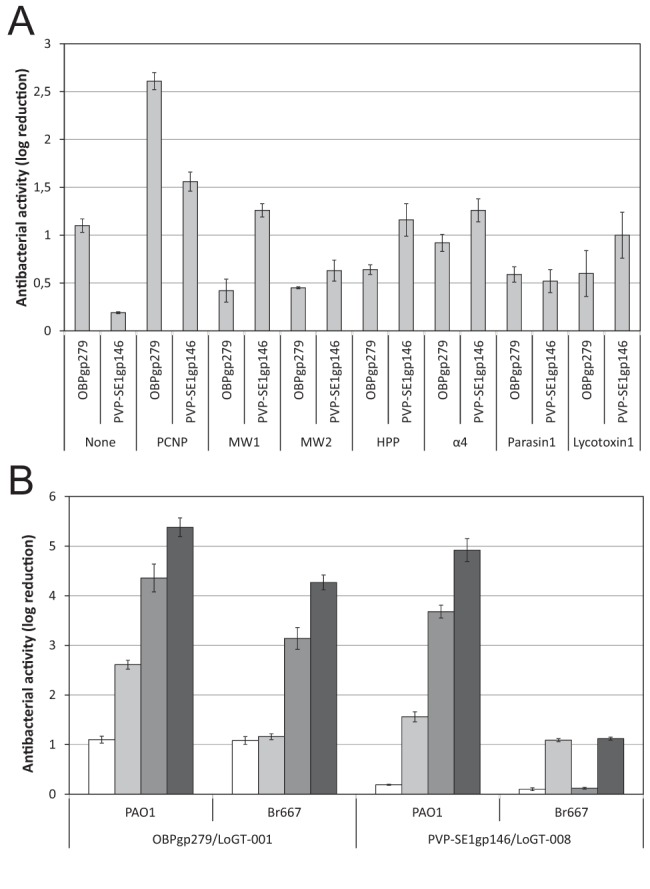
Antibacterial activity of the N-terminal fusion variants of OBPgp279 and PVP-SE1gp146. (A) Fourteen Artilysins with N-terminal fusions of seven different peptides (see Table S1 in the supplemental material) to OBPgp279 and PVP-SE1gp146 are compared to the corresponding unmodified endolysins for their antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa PAO1. This comparison shows the PCNP to be the most effective peptide among the seven peptides tested here. (B) Comparison of the antibacterial activities of two wild-type endolysins (OBPgp279 and PVP-SE1gp146) and their PCNP-tagged Artilysin counterparts (LoGT-001 and LoGT-008, respectively) with and without 0.5 mM EDTA. Activity was tested on P. aeruginosa strains PAO1 and multidrug-resistant Br667, both in the absence (wt endolysin, white bars; Artilysin, light gray bars) and presence (wt endolysin, dark gray bars; Artilysin, black bars) of 0.5 mM EDTA. These data show that the PCNP fusion for the antibacterial activity of the endolysin added value while not compromising its synergy with EDTA. Averages and standard deviations of results of three replicates are shown.
