FIG 1.
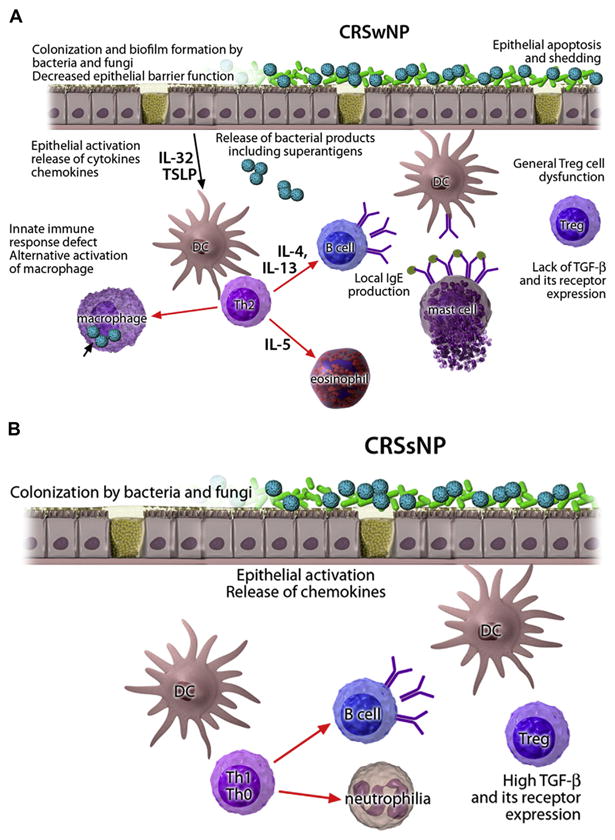
Pathomechanisms of CRS. A, CRSwNP. In a TH2-type microenvironment with general lack of regulatory T (Treg) cell function, IL-5 induces eosinophilia, and IL-4 and IL-13 induce local IgE production. An alternatively activated macrophage subset contributes to the inflammation. The activation of epithelium colonized by bacteria and fungi leads to release of proinflammatory chemokines and cytokines with increased thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and IL-32 levels. Activated epithelial cells die, with apoptosis resulting in a compromised epithelial barrier. B, CRSsNP. Instead of a TH2-skewed T-cell response, a TH1 or a mixed TH0 response predominates, neutrophilia is often associated, and expression of TGF-β and its receptors is increased. DC, Dendritic cell.
