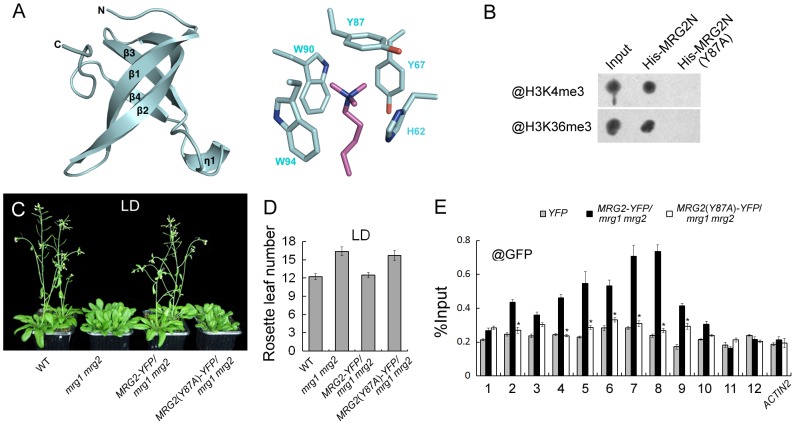
Figure 7. MRG1/2 binding to histone marks is required for their function in regulating flowering.
A. Structure of the MRG2 chromodomain in complex with H3K36me3. The overall structure of the MRG2 chromodomain consisting of four β strands is shown in the left panel. The tri-methylated lysine sticking in the aromatic cage was surrounded by five conserved residues (right panel). Tri-methylated lysine is shown in purple; residues forming the aromatic cage are shown in cyan. B. Binding assays of His-tagged chromodomains of MRG2 (His-MRG2N) and a Y87A substitution in MRG2 chromodomain (His-MRG2N(Y87A)) with H3K4me3 and H3K36me3. C. Phenotypes of wild-type (WT), mrg1 mrg2, PMRG2::MRG2-YFP/mrg1 mrg2 (MRG2-YFP/mrg1 mrg2), and PMRG2::MRG2(Y87A)-YFP/mrg1 mrg2 (MRG2(Y87A)-YFP/mrg1 mrg2) plants grown under long-day photoperiods (LD; 16 h light: 8 h dark), noting that the mrg1 mrg2 double mutants have bolted. D. Flowering time of indicated genotypes, as measured by rosette leaf number at bolting, in plants grown under LD conditions. The mean value from 20 plants is shown. Error bars represent standard deviations. E. ChIP analysis using @GFP at FT chromatin in indicated genotypes at ZT16. Error bars show standard deviation from three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between MRG2(Y87A)-YFP/mrg1 mrg2 plants and MRG2-YFP/mrg1 mrg2 plants (P<0.01).