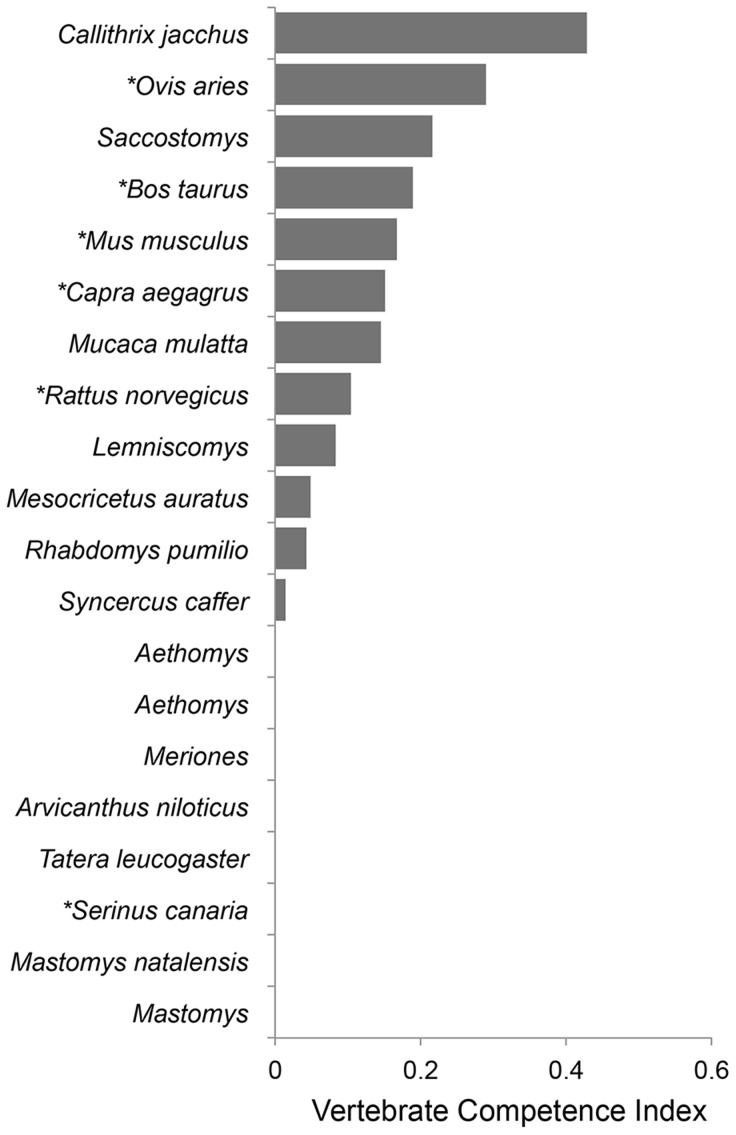
Figure 2. Rift Valley fever virus host competence index values for 20 vertebrate hosts based on experimental infection studies characterizing viremia profiles in PFU/ml or TCID50.
The vertebrate host competence index value depends on the viral titer circulating in the blood and the duration of the infectious viremia [38]. Each value represents the sum of daily probabilities that an infected vertebrate host will transmit RVFV to a biting mosquito. This value was obtained by inserting the recorded daily viremia of experimentally infected hosts into the viremia-vector competence equation [% infectious = 0.062 (Log10 viremia)−0.276 (R2 = 0.27; p<0.001; N = 27)] (Figure S1, C). When a vertebrate host's viremia was calculated to be negative the daily infectiousness was set to zero. Conversion from TCID50 to PFU/ml was obtained by the equation: PFU/ml = TCID50/ml×0.69 [39], [40]. *Denotes a vertebrate species found in the U.S.