Figure 2.
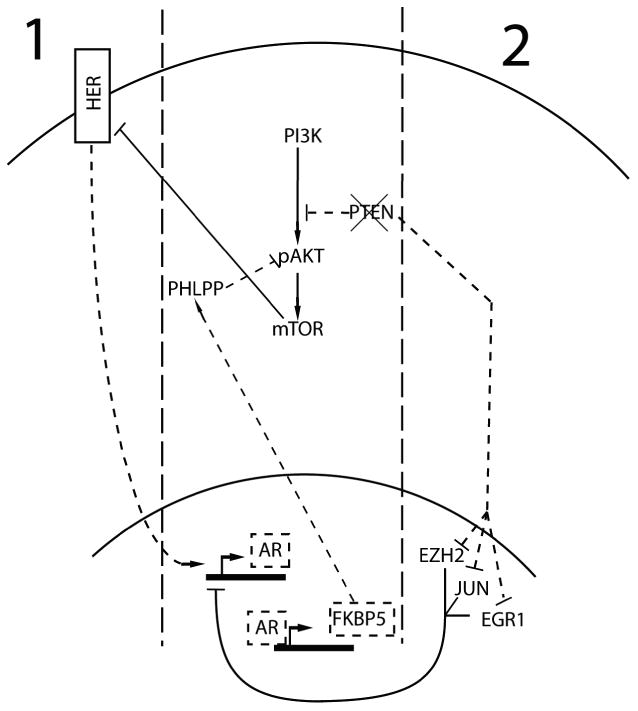
Feedback pathways of AR, PTEN, and PI3K. AR transcriptional activity represses PI3K signaling through the expression of FKBP5. FKBP5 facilitates the dephosphorylation of AKT by PHLPP. PTEN loss, common in prostate cancer, increases PI3K pathway activity and may also repress AR. Two prominent hypotheses explaining the mechanism of PI3K activity and AR repression are presented. 1) Carver et al hypothesize that HER kinases induce expression of AR, and increased PI3K signaling inhibits HER kinases in an mTOR-dependent fashion. This decreases AR expression [28**]. 2) Mullholland et al propose a mechanism by which PTEN negatively regulates the expression and activity of a number of proteins that modulate AR activity (EZH2, JUN, EGR1). PTEN loss deregulates these proteins, repressing AR expression [27**]. Dashed lines indicate pathways where activity is downregulated by PTEN loss.
